Current understanding of TRPM7 pharmacology and drug development for stroke
- PMID: 22820907
- PMCID: PMC4086489
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2012.94
Current understanding of TRPM7 pharmacology and drug development for stroke
Abstract
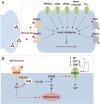
The initial excitement and countless efforts to find a pharmacological agent that disrupts the excitotoxic pathway of ischemic neuronal death have only led to disappointing clinical trials. Currently, a thrombolytic agent called recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rt-PA) is the only pharmacological treatment available for patients with acute ischemic stroke in most countries. Even though its efficacy has been confirmed repeatedly, rt-PA is considerably underused due to reasons including a short therapeutic window and repeated complications associated with its use. A search for alternative mechanisms that may operate dependently or independently with the well-established excitotoxic mechanism has led researchers to the discovery of newly described non-glutamate mechanisms. Among the latter, transient receptor potential melastatin 7 (TRPM7) is one of the important nonglutamate mechanisms in stroke, which has been evaluated in both in-vitro and in-vivo. In this review, we will discuss the current state of pharmacological treatments of ischemic stroke and provide evidence that TRPM7 is a promising therapeutic target of stroke.
Figures
References
-
- Goldstein LB, Bushnell CD, Adams RJ, Appel LJ, Braun LT, Chaturvedi S, et al. Guidelines for the primary prevention of stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2011;42:517–84. - PubMed
-
- Taylor TN, Davis PH, Torner JC, Holmes J, Meyer JW, Jacobson MF. Lifetime cost of stroke in the United States. Stroke. 1996;27:1459–66. - PubMed
-
- Brown DL, Boden-Albala B, Langa KM, Lisabeth LD, Fair M, Smith MA, et al. Projected costs of ischemic stroke in the United States. Neurology. 2006;67:1390–5. - PubMed
-
- Andersen KK, Olsen TS, Dehlendorff C, Kammersgaard LP. Hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes compared: stroke severity, mortality, and risk factors. Stroke. 2009;40:2068–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

