Population pharmacokinetics of clozapine and its primary metabolite norclozapine in Chinese patients with schizophrenia
- PMID: 22820910
- PMCID: PMC4011352
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2012.71
Population pharmacokinetics of clozapine and its primary metabolite norclozapine in Chinese patients with schizophrenia
Abstract
Aim: To develop a combined population pharmacokinetic model (PPK) to assess the magnitude and variability of exposure to both clozapine and its primary metabolite norclozapine in Chinese patients with refractory schizophrenia via sparse sampling with a focus on the effects of covariates on the pharmacokinetic parameters.
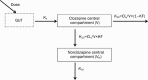
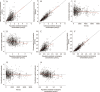
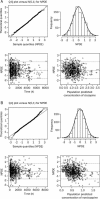
Methods: Relevant patient concentration data (eg, demographic data, medication history, dosage regimen, time of last dose, sampling time, concentrations of clozapine and norclozapine, etc) were collected using a standardized data collection form. The demographic characteristics of the patients, including sex, age, weight, body surface area, smoking status, and information on concomitant medications as well as biochemical and hematological test results were recorded. Persons who had smoked 5 or more cigarettes per day within the last week were defined as smokers. The concentrations of clozapine and norclozapine were measured using a HPLC system equipped with a UV detector. PPK analysis was performed using NONMEM. Age, weight, sex, and smoking status were evaluated as main covariates. The model was internally validated using normalized prediction distribution errors.
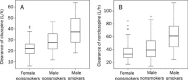
Results: A total of 809 clozapine concentration data sets and 808 norclozapine concentration data sets from 162 inpatients (74 males, 88 females) at multiple mental health sites in China were included. The one-compartment pharmacokinetic model with mixture error could best describe the concentration-time profiles of clozapine and norclozapine. The population-predicted clearance of clozapine and norclozapine in female nonsmokers were 21.9 and 32.7 L/h, respectively. The population-predicted volumes of distribution for clozapine and norclozapine were 526 and 624 L, respectively. Smoking was significantly associated with increases in the clearance (clozapine by 45%; norclozapine by 54.3%). The clearance was significantly greater in males than in females (clozapine by 20.8%; norclozapine by 24.2%). The clearance of clozapine and norclozapine did not differ significantly between Chinese patients and American patients.
Conclusion: Smoking and male were significantly associated with a lower exposure to clozapine and norclozapine due to higher clearance. This model can be used in individualized drug dosing and therapeutic drug monitoring.
Figures
References
-
- Kane J, Honigfeld G, Singer J, Meltzer H. Clozapine for the treatment-resistant schizophrenic. A double-blind comparison with chlorpromazine. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1988;45:789–96. - PubMed
-
- Lieberman JA. Maximizing clozapine therapy: managing side effects. J Clin Psychiatry. 1998;59:38–43. - PubMed
-
- Si TM, Shu L, Yu X, Ma C, Wang GH, Bai PS, et al. The second cross-sectional study on antipsychotic drug patterns of schizophrenia in China. Chin J Psychiatry. 2010;43:31–6.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

