Diversity of P450 enzymes in the biosynthesis of natural products
- PMID: 22820933
- PMCID: PMC3454455
- DOI: 10.1039/c2np20020a
Diversity of P450 enzymes in the biosynthesis of natural products
Abstract
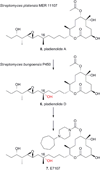
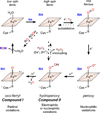
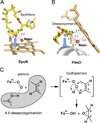
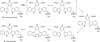
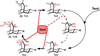
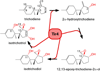
Diverse oxygenation patterns of natural products generated by secondary metabolic pathways in microorganisms and plants are largely achieved through the tailoring reactions catalysed by cytochrome P450 enzymes (P450s). P450s are a large family of oxidative hemoproteins found in all life forms from prokaryotes to humans. Understanding the reactivity and selectivity of these fascinating C-H bond-activating catalysts will advance their use in generating valuable pharmaceuticals and products for medicine, agriculture and industry. A major strength of this P450 group is its set of established enzyme-substrate relationships, the source of the most detailed knowledge on how P450 enzymes work. Engineering microbial-derived P450 enzymes to accommodate alternative substrates and add new functions continues to be an important near- and long-term practical goal driving the structural characterization of these molecules. Understanding the natural evolution of P450 structure-function should accelerate metabolic engineering and directed evolutionary approaches to enhance diversification of natural product structures and other biosynthetic applications.
Figures



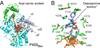

References
-
- Poulos TL, Finzel BC, Gunsalus IC, Wagner GC, Kraut J. J. Biol. Chem. 1985;260:16122–16130. - PubMed
-
- Poulos TL, Finzel BC, Howard AJ. Biochemistry. 1986;25:5314–5322. - PubMed
-
- Poulos TL, Finzel BC, Howard AJ. J. Mol. Biol. 1987;195:687–700. - PubMed
-
- Poulos TL, Howard AJ. Biochemistry. 1987;26:8165–8174. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

