A randomized controlled trial of pretransplant antiviral therapy to prevent recurrence of hepatitis C after liver transplantation
- PMID: 22821361
- PMCID: PMC3510348
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.25976
A randomized controlled trial of pretransplant antiviral therapy to prevent recurrence of hepatitis C after liver transplantation
Abstract
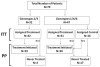
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection recurs in liver recipients who are viremic at transplantation. We conducted a randomized, controlled trial to test the efficacy and safety of pretransplant pegylated interferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin (Peg-IFN-α2b/RBV) for prevention of post-transplant HCV recurrence. Enrollees had HCV and were listed for liver transplantation, with either potential living donors or Model for End-Stage Liver Disease upgrade for hepatocellular carcinoma. Patients with HCV genotypes (G) 1/4/6 (n = 44/2/1) were randomized 2:1 to treatment (n = 31) or untreated control (n = 16); HCV G2/3 (n=32) were assigned to treatment. Overall, 59 were treated and 20 were not. Peg-IFN-α2b, starting at 0.75 μg/kg/week, and RBV, starting at 600 mg/day, were escalated as tolerated. Patients assigned to treatment versus control had similar baseline characteristics. Combined virologic response (CVR) included pretransplant sustained virologic response and post-transplant virologic response (pTVR), defined as undetectable HCV RNA 12 weeks after end of treatment or transplant, respectively. In intent-to-treat analyses, 12 (19%) assigned to treatment and 1 (6%) assigned to control achieved CVR (P = 0.29); per-protocol values were 13 (22%) and 0 (0%) (P = 0.03). Among treated G1/4/6 patients, 23 of 30 received transplant, of whom 22% had pTVR; among treated G2/3 patients 21 of 29 received transplant, of whom 29% had pTVR. pTVR was 0%, 18%, and 50% in patients treated for <8, 8-16, and >16 weeks, respectively (P = 0.01). Serious adverse events (SAEs) occurred with similar frequency in treated versus untreated patients (68% versus 55%; P = 0.30), but the number of SAEs per patient was higher in the treated group (2.7 versus 1.3; P = 0.003).
Conclusion: Pretransplant treatment with Peg-IFN-α2b/RBV prevents post-transplant recurrence of HCV in selected patients. Efficacy is higher with >16 weeks of treatment, but treatment is associated with increased risk of potentially serious complications.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00135798.
Copyright © 2012 American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures



References
-
- Wiesner RH, Sorrell M, Villamil F the International Liver Transplantation Society Expert Panel. Report of the first international liver transplantation society expert panel consensus conference on liver transplantation and hepatitis C. Liver Transpl. 2003;9(Suppl):S1–S9. - PubMed
-
- Forman LM, Lewis JD, Berlin JA, Feldman HI, Lucey MR. The association between hepatitis C infection and survival after orthotopic liver transplantation. Gastroenterology. 2002;122:889–896. - PubMed
-
- Berenguer M. What determines the natural history of recurrent hepatitis C after liver transplantation? J Hepatology. 2005;42:448–456. - PubMed
-
- Charlton M, Wiesner R. Natural history and management of hepatitis C infection after liver transplantation. Semin Liver Dis. 2004;24(Suppl):S79–88. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- DK62505/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062536/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK026743/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062531/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK62484/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK62444/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062498/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062444/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062505/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK62536/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK62531/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062483/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062467/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK62498/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062496/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062484/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK62494/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK62467/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK62483/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK62496/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062494/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
