RNAsnap™: a rapid, quantitative and inexpensive, method for isolating total RNA from bacteria
- PMID: 22821568
- PMCID: PMC3488207
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gks680
RNAsnap™: a rapid, quantitative and inexpensive, method for isolating total RNA from bacteria
Abstract
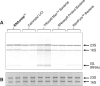
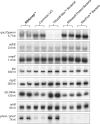
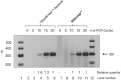
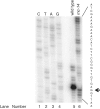
RNAsnap™ is a simple and novel method that recovers all intracellular RNA quantitatively (>99%), faster (<15 min) and less expensively (∼3 cents/sample) than any of the currently available RNA isolation methods. In fact, none of the bacterial RNA isolation methods, including the commercial kits, are effective in recovering all species of intracellular RNAs (76-5700 nt) with equal efficiency, which can lead to biased results in genome-wide studies involving microarray or RNAseq analysis. The RNAsnap™ procedure yields ∼60 µg of RNA from 10(8) Escherichia coli cells that can be used directly for northern analysis without any further purification. Based on a comparative analysis of specific transcripts ranging in size from 76 to 5700 nt, the RNAsnap™ method provided the most accurate measure of the relative amounts of the various intracellular RNAs. Furthermore, the RNAsnap™ RNA was successfully used in enzymatic reactions such as RNA ligation, reverse transcription, primer extension and reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction, following sodium acetate/ethanol precipitation. The RNAsnap™ method can be used to isolate RNA from a wide range of Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria as well as yeast.
Figures
References
-
- Glisin V, Crkvenjakov R, Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974;13:2633–2637. - PubMed
-
- Lin-Chao S, Bremer H. Effect of the bacterial growth rate on replication control of plasmid pBR322 in Esherichia coli. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1986;203:143–149. - PubMed
-
- Chomczynski P, Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal. Biochem. 1987;162:156–159. - PubMed
-
- Macfarlane DE, Dahle CE. Isolating RNA from whole blood-The dawn of RNA-based diagnostics. Nature. 1993;362:186–188. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

