Calcium binding and allosteric signaling mechanisms for the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca²+ ATPase
- PMID: 22821874
- PMCID: PMC3526986
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.2129
Calcium binding and allosteric signaling mechanisms for the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca²+ ATPase
Abstract
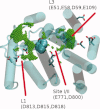
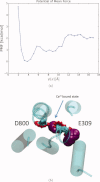
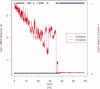
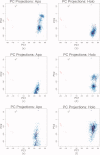
The sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca²⁺ ATPase (SERCA) is a membrane-bound pump that utilizes ATP to drive calcium ions from the myocyte cytosol against the higher calcium concentration in the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Conformational transitions associated with Ca²⁺-binding are important to its catalytic function. We have identified collective motions that partition SERCA crystallographic structures into multiple catalytically-distinct states using principal component analysis. Using Brownian dynamics simulations, we demonstrate the important contribution of surface-exposed, polar residues in the diffusional encounter of Ca²⁺. Molecular dynamics simulations indicate the role of Glu309 gating in binding Ca²⁺, as well as subsequent changes in the dynamics of SERCA's cytosolic domains. Together these data provide structural and dynamical insights into a multistep process involving Ca²⁺ binding and catalytic transitions.
Copyright © 2012 The Protein Society.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Thermodynamics of Cation Binding to the Sarcoendoplasmic Reticulum Calcium ATPase Pump and Impacts on Enzyme Function.J Chem Theory Comput. 2019 Apr 9;15(4):2692-2705. doi: 10.1021/acs.jctc.8b01312. Epub 2019 Mar 13. J Chem Theory Comput. 2019. PMID: 30807147 Free PMC article.
-
The SERCA residue Glu340 mediates interdomain communication that guides Ca2+ transport.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Dec 8;117(49):31114-31122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2014896117. Epub 2020 Nov 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 33229570 Free PMC article.
-
Conformational memory in the association of the transmembrane protein phospholamban with the sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium pump SERCA.J Biol Chem. 2017 Dec 29;292(52):21330-21339. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.794453. Epub 2017 Oct 29. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 29081402 Free PMC article.
-
Ion pathways in the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase.J Biol Chem. 2013 Apr 12;288(15):10759-65. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R112.436550. Epub 2013 Feb 11. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23400778 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The SarcoEndoplasmic Reticulum Calcium ATPase.Subcell Biochem. 2018;87:229-258. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-7757-9_8. Subcell Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29464562 Review.
Cited by
-
Microsecond molecular dynamics simulations of Mg²⁺- and K⁺-bound E1 intermediate states of the calcium pump.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 23;9(4):e95979. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095979. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24760008 Free PMC article.
-
POVME 2.0: An Enhanced Tool for Determining Pocket Shape and Volume Characteristics.J Chem Theory Comput. 2014 Nov 11;10(11):5047-5056. doi: 10.1021/ct500381c. Epub 2014 Sep 29. J Chem Theory Comput. 2014. PMID: 25400521 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for relief of phospholamban-mediated inhibition of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase at saturating Ca2+ conditions.J Biol Chem. 2018 Aug 10;293(32):12405-12414. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.003752. Epub 2018 Jun 22. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29934304 Free PMC article.
-
Linking Biochemical and Structural States of SERCA: Achievements, Challenges, and New Opportunities.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 10;21(11):4146. doi: 10.3390/ijms21114146. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32532023 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiscale computational modeling of the effects of 2'-deoxy-ATP on cardiac muscle calcium handling.J Appl Phys. 2023 Aug 21;134(7):074905. doi: 10.1063/5.0157935. Epub 2023 Aug 16. J Appl Phys. 2023. PMID: 37601331 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Toyoshima C. Structural aspects of ion pumping by Ca2+-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2008;476:3–11. - PubMed
-
- Lewis S, Thomas D. Resolved conformational states of spin-labeled calcium-ATPase during the enzymic cycle. Biochemistry. 1992;31:7381–7389. - PubMed
-
- Toyoshima C, Inesi G. Structural basis of ion pumping by CA(2+)-ATpase of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Biochem. 2004;73:269–292. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

