Glycemic control and chronic dosing of rhesus monkeys with a fusion protein of iduronidase and a monoclonal antibody against the human insulin receptor
- PMID: 22822036
- PMCID: PMC3463822
- DOI: 10.1124/dmd.112.046375
Glycemic control and chronic dosing of rhesus monkeys with a fusion protein of iduronidase and a monoclonal antibody against the human insulin receptor
Abstract
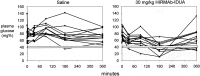
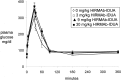
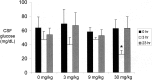
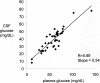
Hurler's syndrome, or mucopolysaccharidosis type I, is a lysosomal storage disorder caused by mutations in the gene encoding the lysosomal enzyme iduronidase (IDUA). The disease affects both peripheral tissues and the central nervous system (CNS). Recombinant IDUA treatment does not affect the CNS, because IDUA does not cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB). To enable BBB penetration, human IDUA was re-engineered as an IgG-IDUA fusion protein, where the IgG domain is a genetically engineered monoclonal antibody (MAb) against the human insulin receptor (HIR). The HIRMAb penetrates the brain from the blood via transport on the endogenous BBB insulin receptor and acts as a molecular Trojan horse to deliver the fused IDUA to the brain. Before human testing, the HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein was evaluated in a 6-month weekly dosing toxicology study at doses of 0, 3, 9, and 30 mg/kg/week of the fusion protein administered to 40 rhesus monkeys. The focus of the present study is the effect of chronic high dose administration of this fusion protein on plasma glucose and long-term glycemic control. The results show that the HIRMAb has weak insulin agonist activity and causes hypoglycemia at the high dose, 30 mg/kg, after intravenous infusion in normal saline. When dextrose is added to the saline infusion solution, no hypoglycemia is observed at any dose. An intravenous glucose tolerance test performed at the end of the 6 months of chronic treatment showed no change in glucose tolerance at any dose of the HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein.
Figures
Similar articles
-
IgG-enzyme fusion protein: pharmacokinetics and anti-drug antibody response in rhesus monkeys.Bioconjug Chem. 2013 Jan 16;24(1):97-104. doi: 10.1021/bc3005123. Epub 2012 Dec 31. Bioconjug Chem. 2013. PMID: 23249376 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic engineering of a lysosomal enzyme fusion protein for targeted delivery across the human blood-brain barrier.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2008 Feb 1;99(2):475-84. doi: 10.1002/bit.21602. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2008. PMID: 17680664
-
Brain and Organ Uptake in the Rhesus Monkey in Vivo of Recombinant Iduronidase Compared to an Insulin Receptor Antibody-Iduronidase Fusion Protein.Mol Pharm. 2017 Apr 3;14(4):1271-1277. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.6b01166. Epub 2017 Mar 16. Mol Pharm. 2017. PMID: 28279069
-
A new generation of neurobiological drugs engineered to overcome the challenges of brain drug delivery.Drug News Perspect. 2008 Nov;21(9):489-503. doi: 10.1358/dnp.2008.21.9.1290820. Drug News Perspect. 2008. PMID: 19180267 Review.
-
Reengineering biopharmaceuticals for targeted delivery across the blood-brain barrier.Methods Enzymol. 2012;503:269-92. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-396962-0.00011-2. Methods Enzymol. 2012. PMID: 22230573 Review.
Cited by
-
Low-Level Endothelial TRAIL-Receptor Expression Obstructs the CNS-Delivery of Angiopep-2 Functionalised TRAIL-Receptor Agonists for the Treatment of Glioblastoma.Molecules. 2021 Dec 14;26(24):7582. doi: 10.3390/molecules26247582. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34946664 Free PMC article.
-
The Challenge of Modulating Heparan Sulfate Turnover by Multitarget Heparin Derivatives.Molecules. 2020 Jan 17;25(2):390. doi: 10.3390/molecules25020390. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 31963505 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigating receptor-mediated antibody transcytosis using blood-brain barrier organoid arrays.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2021 Sep 20;18(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s12987-021-00276-x. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2021. PMID: 34544422 Free PMC article.
-
Current progress in innovative engineered antibodies.Protein Cell. 2018 Jan;9(1):86-120. doi: 10.1007/s13238-017-0457-8. Epub 2017 Aug 18. Protein Cell. 2018. PMID: 28822103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanobodies as modulators of inflammation: potential applications for acute brain injury.Front Cell Neurosci. 2014 Oct 21;8:344. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00344. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25374510 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boado RJ, Hui EK, Lu JZ, Zhou QH, Pardridge WM. (2011) Reversal of lysosomal storage in brain of adult MPS-I mice with intravenous Trojan horse-iduronidase fusion protein. Mol Pharm 8:1342–1350 - PubMed
-
- Boado RJ, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Xia CF, Wang Y, Pardridge WM. (2008) Genetic engineering of a lysosomal enzyme fusion protein for targeted delivery across the human blood-brain barrier. Biotechnol Bioeng 99:475–484 - PubMed
-
- Brady RO, Schiffmann R. (2004) Enzyme-replacement therapy for metabolic storage disorders. Lancet Neurol 3:752–756 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

