A novel biotinylated lipid raft reporter for electron microscopic imaging of plasma membrane microdomains
- PMID: 22822037
- PMCID: PMC3435554
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.D026468
A novel biotinylated lipid raft reporter for electron microscopic imaging of plasma membrane microdomains
Abstract
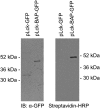
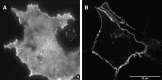
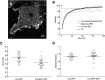
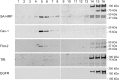
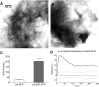
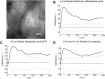
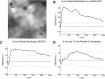
The submicroscopic spatial organization of cell surface receptors and plasma membrane signaling molecules is readily characterized by electron microscopy (EM) via immunogold labeling of plasma membrane sheets. Although various signaling molecules have been seen to segregate within plasma membrane microdomains, the biochemical identity of these microdomains and the factors affecting their formation are largely unknown. Lipid rafts are envisioned as submicron membrane subdomains of liquid ordered structure with differing lipid and protein constituents that define their specific varieties. To facilitate EM investigation of inner leaflet lipid rafts and the localization of membrane proteins therein, a unique genetically encoded reporter with the dually acylated raft-targeting motif of the Lck kinase was developed. This reporter, designated Lck-BAP-GFP, incorporates green fluorescent protein (GFP) and biotin acceptor peptide (BAP) modules, with the latter allowing its single-step labeling with streptavidin-gold. Lck-BAP-GFP was metabolically biotinylated in mammalian cells, distributed into low-density detergent-resistant membrane fractions, and was readily detected with avidin-based reagents. In EM images of plasma membrane sheets, the streptavidin-gold-labeled reporter was clustered in 20-50 nm microdomains, presumably representative of inner leaflet lipid rafts. The utility of the reporter was demonstrated in an investigation of the potential lipid raft localization of the epidermal growth factor receptor.
Figures

References
-
- Simons K., Toomre D. 2000. Lipid rafts and signal transduction. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 1: 31–39 - PubMed
-
- Tian T., Harding A., Inder K., Plowman S., Parton R. G., Hancock J. F. 2007. Plasma membrane nanoswitches generate high-fidelity Ras signal transduction. Nat. Cell Biol. 9: 905–914 - PubMed
-
- Wilson B. S., Pfeiffer J. R., Oliver J. M. 2002. FcepsilonRI signaling observed from the inside of the mast cell membrane. Mol. Immunol. 38: 1259–1268 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

