Ca2+ regulation of ion transport in the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger
- PMID: 22822067
- PMCID: PMC3442498
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.R112.353573
Ca2+ regulation of ion transport in the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger
Abstract
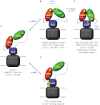
The binding of Ca(2+) to two adjacent Ca(2+)-binding domains, CBD1 and CBD2, regulates ion transport in the Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchanger. As sensors for intracellular Ca(2+), the CBDs form electrostatic switches that induce the conformational changes required to initiate and sustain Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchange. Depending on the presence of a few key residues in the Ca(2+)-binding sites, zero to four Ca(2+) ions can bind with affinities between 0.1 to 20 μm. Importantly, variability in CBD2 as a consequence of alternative splicing modulates not only the number and affinities of the Ca(2+)-binding sites in CBD2 but also the Ca(2+) affinities in CBD1.
Figures

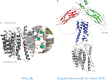
References
-
- Blaustein M. P., Lederer W. J. (1999) Sodium/calcium exchange: its physiological implications. Physiol. Rev. 79, 763–854 - PubMed
-
- Philipson K. D., Nicoll D. A. (2000) Sodium/calcium exchange: a molecular perspective. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 62, 111–133 - PubMed
-
- Annunziato L., Pignataro G., Di Renzo G. F. (2004) Pharmacology of brain Na+/Ca2+ exchanger: from molecular biology to therapeutic perspectives. Pharmacol. Rev. 56, 633–654 - PubMed
-
- Lytton J. (2007) Na+/Ca2+ exchangers: three mammalian gene families control Ca2+ transport. Biochem. J. 406, 365–382 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

