Rituximab in idiopathic membranous nephropathy
- PMID: 22822077
- PMCID: PMC3402291
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2012020181
Rituximab in idiopathic membranous nephropathy
Abstract
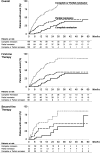
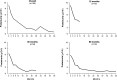
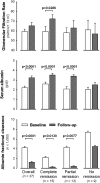
Selective depletion of B cells with the mAb rituximab may benefit the autoimmune glomerular disease idiopathic membranous nephropathy (IMN). Here, we describe our experience treating 100 consecutive IMN patients with persistent nephrotic syndrome with rituximab. We defined complete remission as persistent proteinuria <0.3 g/24 h and partial remission as persistent proteinuria <3 g/24 h, each also having >50% reduction in proteinuria from baseline. During a median follow-up of 29 months after rituximab administration, 65 patients achieved complete or partial remission. The median time to remission was 7.1 months. All 24 patients who had at least 4 years of follow-up achieved complete or partial remission. Rates of remission were similar between patients with or without previous immunosuppressive treatment. Four patients died and four progressed to ESRD. Measured GFR increased by a mean 13.2 (SD 19.6) ml/min per 1.73 m(2) among those who achieved complete remission. Serum albumin significantly increased and albumin fractional clearance decreased among those achieving complete or partial remission. Proteinuria at baseline and the follow-up duration each independently predicted the decline of proteinuria. Furthermore, the magnitude of proteinuria reduction significantly correlated with slower GFR decline (P=0.0001). No treatment-related serious adverse events occurred. In summary, rituximab achieved disease remission and stabilized or improved renal function in a large cohort of high-risk patients with IMN.
Figures

Comment in
-
Rituximab in membranous nephropathy: is it a first-line treatment?J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012 Aug;23(8):1280-2. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2012060602. Epub 2012 Jul 12. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22797189 No abstract available.
-
Glomerular disease: rituximab promising for idiopathic membranous nephropathy.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2012 Oct;8(10):556. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2012.184. Epub 2012 Aug 7. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22868704 No abstract available.
-
What is the role of rituximab in idiopathic membranous nephropathy?Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2013 Jan;9(1):13-6. doi: 10.1586/eci.12.89. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23256760
References
-
- Austin HA, 3rd, Antonovych TT, MacKay K, Boumpas DT, Balow JE: NIH conference. Membranous nephropathy. Ann Intern Med 116: 672–682, 1992 - PubMed
-
- Schieppati A, Mosconi L, Perna A, Mecca G, Bertani T, Garattini S, Remuzzi G: Prognosis of untreated patients with idiopathic membranous nephropathy. N Engl J Med 329: 85–89, 1993 - PubMed
-
- Polanco N, Gutiérrez E, Covarsí A, Ariza F, Carreño A, Vigil A, Baltar J, Fernández-Fresnedo G, Martín C, Pons S, Lorenzo D, Bernis C, Arrizabalaga P, Fernández-Juárez G, Barrio V, Sierra M, Castellanos I, Espinosa M, Rivera F, Oliet A, Fernández-Vega F, Praga M, Grupo de Estudio de las Enfermedades Glomerulares de la Sociedad Española de Nefrología : Spontaneous remission of nephrotic syndrome in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 21: 697–704, 2010 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ruggenenti P, Cravedi P, Remuzzi G: Latest treatment strategies for membranous nephropathy. Expert Opin Pharmacother 8: 3159–3171, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Jha V, Ganguli A, Saha TK, Kohli HS, Sud K, Gupta KL, Joshi K, Sakhuja V: A randomized, controlled trial of steroids and cyclophosphamide in adults with nephrotic syndrome caused by idiopathic membranous nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 18: 1899–1904, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

