Phosphatidylinositol transfer protein, cytoplasmic 1 (PITPNC1) binds and transfers phosphatidic acid
- PMID: 22822086
- PMCID: PMC3442557
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.375840
Phosphatidylinositol transfer protein, cytoplasmic 1 (PITPNC1) binds and transfers phosphatidic acid
Abstract
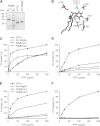
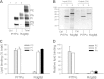
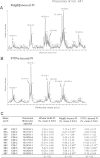
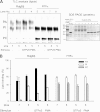
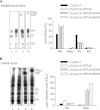
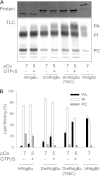
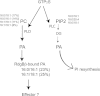
Phosphatidylinositol transfer proteins (PITPs) are versatile proteins required for signal transduction and membrane traffic. The best characterized mammalian PITPs are the Class I PITPs, PITPα (PITPNA) and PITPβ (PITPNB), which are single domain proteins with a hydrophobic cavity that binds a phosphatidylinositol (PI) or phosphatidylcholine molecule. In this study, we report the lipid binding properties of an uncharacterized soluble PITP, phosphatidylinositol transfer protein, cytoplasmic 1 (PITPNC1) (alternative name, RdgBβ), of the Class II family. We show that the lipid binding properties of this protein are distinct to Class I PITPs because, besides PI, RdgBβ binds and transfers phosphatidic acid (PA) but hardly binds phosphatidylcholine. RdgBβ when purified from Escherichia coli is preloaded with PA and phosphatidylglycerol. When RdgBβ was incubated with permeabilized HL60 cells, phosphatidylglycerol was released, and PA and PI were now incorporated into RdgBβ. After an increase in PA levels following activation of endogenous phospholipase D or after addition of bacterial phospholipase D, binding of PA to RdgBβ was greater at the expense of PI binding. We propose that RdgBβ, when containing PA, regulates an effector protein or can facilitate lipid transfer between membrane compartments.
Figures





References
-
- Cockcroft S., Garner K. (2011) Function of the phosphatidylinositol transfer protein gene family: is phosphatidylinositol transfer the mechanism of action? Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 46, 89–117 - PubMed
-
- Allen-Baume V., Ségui B., Cockcroft S. (2002) Current thoughts on the phosphatidylinositol transfer protein family. FEBS Lett. 531, 74–80 - PubMed
-
- Yoder M. D., Thomas L. M., Tremblay J. M., Oliver R. L., Yarbrough L. R., Helmkamp G. M., Jr. (2001) Structure of a multifunctional protein. Mammalian phosphatidylinositol transfer protein complexed with phosphatidylcholine. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 9246–9252 - PubMed
-
- Tilley S. J., Skippen A., Murray-Rust J., Swigart P. M., Stewart A., Morgan C. P., Cockcroft S., McDonald N. Q. (2004) Structure-function analysis of human [corrected] phosphatidylinositol transfer protein α bound to phosphatidylinositol. Structure 12, 317–326 - PubMed
-
- Vordtriede P. B., Doan C. N., Tremblay J. M., Helmkamp G. M., Jr., Yoder M. D. (2005) Structure of PITPβ in complex with phosphatidylcholine: comparison of structure and lipid transfer to other PITP isoforms. Biochemistry 44, 14760–14771 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

