Progesterone directly and rapidly inhibits GnRH neuronal activity via progesterone receptor membrane component 1
- PMID: 22822163
- PMCID: PMC3423625
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2012-1122
Progesterone directly and rapidly inhibits GnRH neuronal activity via progesterone receptor membrane component 1
Abstract
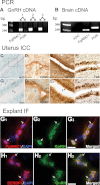
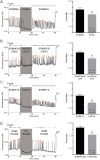
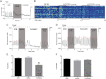
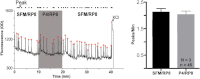
GnRH neurons are essential for reproduction, being an integral component of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis. Progesterone (P4), a steroid hormone, modulates reproductive behavior and is associated with rapid changes in GnRH secretion. However, a direct action of P4 on GnRH neurons has not been previously described. Receptors in the progestin/adipoQ receptor family (PAQR), as well as progesterone receptor membrane component 1 (PgRMC1) and its partner serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade E (nexin, plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1) mRNA binding protein 1 (SERBP1), have been shown to mediate rapid progestin actions in various tissues, including the brain. This study shows that PgRMC1 and SERBP1, but not PAQR, are expressed in prenatal GnRH neurons. Expression of PgRMC1 and SERBP1 was verified in adult mouse GnRH neurons. To investigate the effect of P4 on GnRH neuronal activity, calcium imaging was used on primary GnRH neurons maintained in explants. Application of P4 significantly decreased the activity of GnRH neurons, independent of secretion of gamma-aminobutyric acidergic and glutamatergic input, suggesting a direct action of P4 on GnRH neurons. Inhibition was not blocked by RU486, an antagonist of the classic nuclear P4 receptor. Inhibition was also maintained after uncoupling of the inhibitory regulative G protein (G(i/o)), the signal transduction pathway used by PAQR. However, AG-205, a PgRMC1 ligand and inhibitor, blocked the rapid P4-mediated inhibition, and inhibition of protein kinase G, thought to be activated downstream of PgRMC1, also blocked the inhibitory activity of P4. These data show for the first time that P4 can act directly on GnRH neurons through PgRMC1 to inhibit neuronal activity.
Figures

References
-
- Goodman RL, Karsch FJ. 1980. Pulsatile secretion of luteinizing hormone: differential suppression by ovarian steroids. Endocrinology 107:1286–1290 - PubMed
-
- Levine JE, Pau KY, Ramirez VD, Jackson GL. 1982. Simultaneous measurement of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone and luteinizing hormone release in unanesthetized, ovariectomized sheep. Endocrinology 111:1449–1455 - PubMed
-
- Gross KM, Matsumoto AM, Bremner WJ. 1987. Differential control of luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone secretion by luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone pulse frequency in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 64:675–680 - PubMed
-
- Marshall JC, Kelch RP. 1986. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone: role of pulsatile secretion in the regulation of reproduction. N Engl J Med 315:1459–1468 - PubMed
-
- Wildt L, Häusler A, Marshall G, Hutchison JS, Plant TM, Belchetz PE, Knobil E. 1981. Frequency and amplitude of gonadotropin-releasing hormone stimulation and gonadotropin secretion in the rhesus monkey. Endocrinology 109:376–385 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

