Intensification of insulin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: an algorithm for basal-bolus therapy
- PMID: 22822902
- PMCID: PMC3529158
- DOI: 10.3109/07853890.2012.699715
Intensification of insulin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: an algorithm for basal-bolus therapy
Abstract
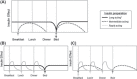
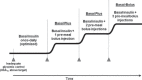
The incidence of diabetes mellitus is projected to continue to increase worldwide over the next 20 years leading to increased costs in the management of the disease and its associated co-morbidities. Insulin replacement is one of many treatment options that can help to bring about near normoglycemia in the patient with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Glycemic control as close to normoglycemia as possible can help to reduce the risk of microvascular and macrovascular complications, yet less than one-half of patients with T2DM achieve glycemic targets as recommended by practice guidelines. The purpose of this review is to provide guidance to primary care physicians for the initiation and intensification of basal-bolus insulin therapy in patients with T2DM. Two treatment algorithms that can be both patient- and physician-driven are proposed: a stepwise approach and a multiple daily injections approach. Evidence shaping the two approaches will be discussed alongside management issues that surround the patient treated with insulin: hypoglycemia, weight gain, patient education, and quality of life.
Figures


References
-
- International Diabetes Federation. Diabetes Backgrounder. http://www.eatlas.idf.org/webdata/docs/background_opening_pc.pdf
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Centers for Disease Control detailed data for diagnosed diabetes. http://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/statistics/prev/national/tnumage.htm
-
- Patel A, MacMahon S, Chalmers J, Neal B, Billot L, Woodward M, et al. Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:2560–72. - PubMed
-
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:977–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
