Glucocorticoid regulation of inflammation and its functional correlates: from HPA axis to glucocorticoid receptor dysfunction
- PMID: 22823394
- PMCID: PMC3572859
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2012.06633.x
Glucocorticoid regulation of inflammation and its functional correlates: from HPA axis to glucocorticoid receptor dysfunction
Abstract
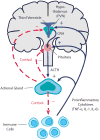
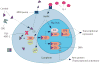
Enhanced susceptibility to inflammatory and autoimmune disease can be related to impairments in HPA axis activity and associated hypocortisolism, or to glucocorticoid resistance resulting from impairments in local factors affecting glucocorticoid availability and function, including the glucocorticoid receptor (GR). The enhanced inflammation and hypercortisolism that typically characterize stress-related illnesses, such as depression, metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular disease, or osteoporosis, may also be related to increased glucocorticoid resistance. This review focuses on impaired GR function as a molecular mechanism of glucocorticoid resistance. Both genetic and environmental factors can contribute to impaired GR function. The evidence that glucocorticoid resistance can be environmentally induced has important implications for management of stress-related inflammatory illnesses and underscores the importance of prevention and management of chronic stress. The simultaneous assessment of neural, endocrine, and immune biomarkers through various noninvasive methods will also be discussed.
© 2012 New York Academy of Sciences. No claim to original U.S. Government works.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sapolsky RM, Romero LM, Munck AU. How do glucocorticoids influence stress responses? Integrating permissive, suppressive, stimulatory, and preparative actions. Endocr Rev. 2000;21:55–89. - PubMed
-
- Besedovsky HO, del Rey A. Immune-neuro-endocrine interactions: facts and hypotheses. Endocr Rev. 1996;17:64–102. - PubMed
-
- McEwen BS, et al. The role of adrenocorticoids as modulators of immune function in health and disease: neural, endocrine and immune interactions. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1997;23:79–133. - PubMed
-
- Webster JI, Sternberg EM. Role of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, glucocorticoids and glucocorticoid receptors in toxic sequelae of exposure to bacterial and viral products. J Endocrinol. 2004;181:207–221. - PubMed
-
- Glezer I, Rivest S. Glucocorticoids: protectors of the brain during innate immune responses. Neuroscientist. 2004;10:538–552. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

