Influence of gravity compensation training on synergistic movement patterns of the upper extremity after stroke, a pilot study
- PMID: 22824488
- PMCID: PMC3443435
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-0003-9-44
Influence of gravity compensation training on synergistic movement patterns of the upper extremity after stroke, a pilot study
Abstract
Background: The majority of stroke patients have to cope with impaired arm function. Gravity compensation of the arm instantaneously affects abnormal synergistic movement patterns. The goal of the present study is to examine whether gravity compensated training improves unsupported arm function.
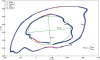
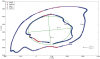
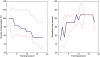
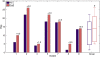
Methods: Seven chronic stroke patients received 18 half-hour sessions of gravity compensated reach training, in a period of six weeks. During training a motivating computer game was played. Before and after training arm function was assessed with the Fugl-Meyer assessment and a standardized, unsupported circle drawing task. Synergistic movement patterns were identified based on concurrent changes in shoulder elevation and elbow flexion/extension angles.
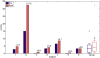
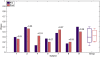
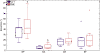
Results: Median increase of Fugl-Meyer scores was 3 points after training. The training led to significantly increased work area of the hemiparetic arm, as indicated by the normalized circle area. Roundness of the drawn circles and the occurrence of synergistic movement patterns remained similar after the training.
Conclusions: A decreased strength of involuntary coupling might contribute to the increased arm function after training. More research is needed to study working mechanisms involved in post stroke rehabilitation training. The used training setup is simple and affordable and is therefore suitable to use in clinical settings.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Preliminary results of training with gravity compensation of the arm in chronic stroke survivors.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2009;2009:2426-9. doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.2009.5335288. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2009. PMID: 19965202
-
Changes in muscle activation after reach training with gravity compensation in chronic stroke patients.Int J Rehabil Res. 2012 Sep;35(3):234-42. doi: 10.1097/MRR.0b013e328353e3f1. Int J Rehabil Res. 2012. PMID: 22555316
-
Influence of gravity compensation on muscle activation patterns during different temporal phases of arm movements of stroke patients.Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2009 Jun;23(5):478-85. doi: 10.1177/1545968308328720. Epub 2009 Feb 3. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2009. PMID: 19190089
-
Circle drawing as evaluative movement task in stroke rehabilitation: an explorative study.J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2011 Mar 24;8:15. doi: 10.1186/1743-0003-8-15. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2011. PMID: 21435261 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
An explorative study into changes in circle drawing after gravity compensation training in chronic stroke patients.IEEE Int Conf Rehabil Robot. 2011;2011:5975402. doi: 10.1109/ICORR.2011.5975402. IEEE Int Conf Rehabil Robot. 2011. PMID: 22275605
Cited by
-
Robot-supported upper limb training in a virtual learning environment : a pilot randomized controlled trial in persons with MS.J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2015 Jul 23;12:60. doi: 10.1186/s12984-015-0043-3. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2015. PMID: 26202325 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of Sling-Suspension-Based Active Shoulder Joint Exercise on Shoulder Joint Subluxation, Pain, Muscle Strength, and Upper Limb Function in Patients with Subacute Stroke.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Aug 20;60(8):1350. doi: 10.3390/medicina60081350. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39202631 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Serious Games Strategies With Cable-Driven Robots for Bimanual Rehabilitation: A Randomized Controlled Trial With Post-Stroke Patients.Front Robot AI. 2022 Feb 17;9:739088. doi: 10.3389/frobt.2022.739088. eCollection 2022. Front Robot AI. 2022. PMID: 35252362 Free PMC article.
-
Optimizing shoulder elevation assist rate in exoskeletal rehabilitation based on muscular activity indices: a clinical feasibility study.BMC Neurol. 2024 May 9;24(1):144. doi: 10.1186/s12883-024-03651-x. BMC Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38724916 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of arm weight support on neuromuscular activation during reaching in chronic stroke patients.Exp Brain Res. 2019 Dec;237(12):3391-3408. doi: 10.1007/s00221-019-05687-9. Epub 2019 Nov 14. Exp Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 31728596
References
-
- Chae J, Yang G, Park BK, Labatia I. Muscle weakness and cocontraction in upper limb hemiparesis: relationship to motor impairment and physical disability. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2002;16(3):241–248. - PubMed
-
- Brunnstrom S. Movement therapy in hemiplegia, a neurophysiological approach. Harper & Row Publishers Inc, New York; 1970.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

