Transcriptional regulation of the 5-HT1A receptor: implications for mental illness
- PMID: 22826341
- PMCID: PMC3405675
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2011.0376
Transcriptional regulation of the 5-HT1A receptor: implications for mental illness
Abstract
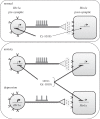
The serotonin-1A (5-HT(1A)) receptor is an abundant post-synaptic 5-HT receptor (heteroreceptor) implicated in regulation of mood, emotion and stress responses and is the major somatodendritic autoreceptor that negatively regulates 5-HT neuronal activity. Based on animal models, an integrated model for opposing roles of pre- and post-synaptic 5-HT(1A) receptors in anxiety and depression phenotypes and response to antidepressants is proposed. Understanding differential transcriptional regulation of pre- versus post-synaptic 5-HT(1A) receptors could provide better tools for their selective regulation. This review examines the transcription factors that regulate brain region-specific basal and stress-induced expression of the 5-HT(1A) receptor gene (Htr1a). A functional polymorphism, rs6295 in the Htr1a promoter region, blocks the function of specific repressors Hes1, Hes5 and Deaf1, resulting in increased 5-HT(1A) autoreceptor expression in animal models and humans. Its association with altered 5-HT(1A) expression, depression, anxiety and antidepressant response are related to genotype frequency in different populations, sample homogeneity, disease outcome measures and severity. Preliminary evidence from gene × environment studies suggests the potential for synergistic interaction of stress-mediated repression of 5-HT(1A) heteroreceptors, and rs6295-induced upregulation of 5-HT(1A) autoreceptors. Targeted therapeutics to inhibit 5-HT(1A) autoreceptor expression and induce 5-HT(1A) heteroreceptor expression may ameliorate treatment of anxiety and major depression.
Figures
References
-
- Anden N. E., Carlsson A., Haggendal J. 1969. Adrenergic mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. 9, 119–13410.1146/annurev.pa.09.040169.001003 (doi:10.1146/annurev.pa.09.040169.001003) - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Carlsson A. 1975. Dopamine autoreceptors. In Chemical tools in catecholamine research (eds Almgren O., Carlsson A., Engel J.), pp. 219–225 Amsterdam, The Netherlands: North-Holland
-
- Starke K., Gothert M., Kilbinger H. 1989. Modulation of neurotransmitter release by presynaptic autoreceptors. Physiol. Rev. 69, 864–989 - PubMed
-
- Gothert M. 1982. Modulation of serotonin release in the brain via presynaptic receptors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 3, 437–44010.1016/0165-6147(82)91222-6 (doi:10.1016/0165-6147(82)91222-6) - DOI - DOI
-
- Aghajanian G. K. 1982. Regulation of serotonergic neuronal activity: autoreceptors and pacemaker potentials. Adv. Biochem. Psychopharmacol. 34, 173–181 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
