Africa has unique and urgent barriers to cleft care: lessons from practitioners at the Pan-African Congress on Cleft Lip and Palate
- PMID: 22826739
- PMCID: PMC3396861
Africa has unique and urgent barriers to cleft care: lessons from practitioners at the Pan-African Congress on Cleft Lip and Palate
Abstract
Background: The goals of this study were to delineate the protocols employed for managing patients with cleft lip and palate deformities, delineate the challenges facing practitioners and patients, and to determine the patient and physician barriers to cleft care delivery in the region.
Methods: Survey questionnaires were administered to practitioners attending the second Pan-African Congress on Cleft Lip and Palate (PACCLIP), which took place in Ibadan, Nigeria, West Africa from February 4-7, 2007. The conference included 225 participants, representing 17 African countries
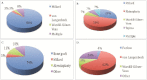
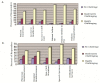
Results: Protocols for repair of cleft lip and palate deformities were varied, with Millard's and von Langenbeck's techniques being the preferred approach for the management of cleft lip and palate deformities, respectively. A large proportion of providers have limited access to core cleft care supporting teams, especially speech language pathologists, orthodontists, and audiologists. Several challenging barriers to cleft care were also identified at both the institutional and individual levels and are reported.
Conclusion: Geographic separation in Africa presents a similar challenge due to isolationism as it does to surgeons in Europe. Specific to Africa are the increased barriers to care, and economic and financial hardship at various levels. A focus on funding, team building, infrastructural support, and patient education appear to be crucial in improving the care and lives of children with facial clefts in Africa.
Keywords: Africa; Cleft care; Nigeria; cleft Palate; cleft lip; craniofacial cleft.
Figures




References
-
- Petersen PE. The World Oral Health Report; 2003. World Health Organization. Available at: http://www.who.int/oral_health/media/en/orh_report03_en.pdf. Accessed 9 March 2012.
-
- Suleiman AM, Hamzah ST, Abusalab MA, Samaan KT. Prevalence of cleft lip and palate in a hospital-based population in the Sudan. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2005;15(3):185–189. - PubMed
-
- Donkor P, Plange-Rhule G, Amponsah EK. A prospective survey of patients with cleft lip and palate in Kumasi. West Afr J Med. 2007;26(1):14–16. - PubMed
-
- Olasoji HO, Ukiri OE, Yahaya A. Incidence and aetiology of oral clefts: a review. Afr J Med Med Sci. 2005;34(1):1–7. - PubMed
-
- Iregbulem LM. The incidence of cleft lip and palate in Nigeria. Cleft Palate J. 1982;19(3):201–205. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
