Mental disorder prevention and physical activity in Iranian elderly
- PMID: 22826772
- PMCID: PMC3399311
Mental disorder prevention and physical activity in Iranian elderly
Abstract
Objectives: Mental disorders such as depression, anxiety and dementia are common in elderly. However, physical activity is suggested to be effective in preventing such aging-related disorders. The aim of this study was to investigate the role of physical activity on mental health in later life.
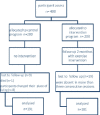
Methods: Four hundred elderly people were randomly divided into the intervention and control groups. The intervention consisted of exercise twice a week for two months. Mental health status before, just after, and three months after the study was assessed with the 28-item General Health Questionnaire (GHQ-28).
Results: The mean of the GHQ-28 total scale decreased in the case group and this change remained significant after three months (before: 8 ± 5.5, after three months: 5.6 ± 4.6, p < .001). GHQ subscales including somatization, anxiety, social dysfunction, and depression decreased significantly in the case group just after and three months after the intervention.
Conclusions: Physical activity significantly prevents mental disorder in older adults. Although it has effects on anxiety, social dysfunction, and depression, the greatest influence is on improving the somatization symptoms.
Keywords: Aging; GHQ-28; mental health; physical activity.
Conflict of interest statement
References
-
- Drewnowski A, Evans WJ. Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Quality of Life in Older Adults: Summary. J Gerontol. 2001;56:89–94. - PubMed
-
- Bastone AdC, Filho WJ. Effect of an exercise program on functional performance of institutionalized elderly. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2004;41:659–68. - PubMed
-
- Mirzai M, Shams M. Demograghy of elder population in Iran over the period 1956 to 2006. Iran J Aging Res. 2007;5:226–31.
-
- Center for Health Workforce Studies School of Public Health. The impact of aging population on the health workforce in the United States. University at Albany. National Center for Health Workforce Analysis. 2006. [Last cited on 2011 Apr 09]. Available from: http://www.albany.edu/news/pdf_files/impact_of_aging_full.pdf .
-
- Sherina M, Rampal LS, Aini M, Norhidayati HM. The prevalence of depression among elderly in an urban area of Selangor, Malaysia. Int Med J. 2005;4:57–63.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources