The amygdala as a target for behavior surgery
- PMID: 22826810
- PMCID: PMC3400485
- DOI: 10.4103/2152-7806.91609
The amygdala as a target for behavior surgery
Abstract
The amygdala was a popular target during the era of psychosurgery, specifically for the treatment of intractable aggression. This mesiotemporal structure was thought to primarily mediate fear and anger. However, recent evidence suggests that the amygdala is part of a complex network that mediates the formation of a larger repertoire of positive and negative emotions. Dysfunctions within the network or the amygdala itself can lead to various mental illnesses. In those cases, deep brain stimulation (DBS) applied focally may treat the symptoms. This review presents data supporting the potential therapeutic role of DBS of the amygdala in the treatment of anxiety disorders, addiction, and mood disorders. The success of DBS for psychiatric conditions will likely depend on our ability to precisely determine the optimal target for a specific case.
Keywords: Addiction; amygdala; deep brain stimulation; depression; post-traumatic stress disorder.
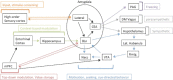
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prefrontal Cortex Deep Brain Stimulation Improves Fear and Anxiety-Like Behavior and Reduces Basolateral Amygdala Activity in a Preclinical Model of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018 Apr;43(5):1099-1106. doi: 10.1038/npp.2017.207. Epub 2017 Sep 1. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018. PMID: 28862251 Free PMC article.
-
Deep brain stimulation of the amygdala alleviates post-traumatic stress disorder symptoms in a rat model.J Psychiatr Res. 2010 Dec;44(16):1241-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2010.04.022. Epub 2010 May 26. J Psychiatr Res. 2010. PMID: 20537659
-
Deep Brain Stimulation for Intractable Obsessive-compulsive Disorder: The International and Japanese Situation/Scenario.Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2018 Sep 15;58(9):369-376. doi: 10.2176/nmc.st.2018-0115. Epub 2018 Aug 9. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2018. PMID: 30089754 Free PMC article.
-
Stereotactic lesions for the treatment of psychiatric disorders.J Neurosurg. 2010 Dec;113(6):1204-11. doi: 10.3171/2010.5.JNS091277. Epub 2010 Jun 18. J Neurosurg. 2010. PMID: 20560726 Review.
-
Nucleus Accumbens as a Novel Target for Deep Brain Stimulation in the Treatment of Addiction: A Hypothesis on the Neurochemical and Morphological Basis.Neurol India. 2019 Sep-Oct;67(5):1220-1224. doi: 10.4103/0028-3886.271239. Neurol India. 2019. PMID: 31744946 Review.
Cited by
-
Case report: stimulation of the right amygdala induces transient changes in affective bias.Brain Stimul. 2014 Sep-Oct;7(5):690-3. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2014.05.005. Epub 2014 May 24. Brain Stimul. 2014. PMID: 24972588 Free PMC article.
-
Relations of Psychosocial Factors and Cortisol with Periodontal and Bacterial Parameters: A Prospective Clinical Study in 30 Patients with Periodontitis Before and After Non-Surgical Treatment.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Oct 20;17(20):7651. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17207651. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33092182 Free PMC article.
-
Treating Aggression and Self-destructive Behaviors by Stimulating the Nucleus Accumbens: A Case Series.Front Neurol. 2021 Oct 11;12:706166. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.706166. eCollection 2021. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34707553 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional neural adaptations in obstructive sleep apnea: An activation likelihood estimation meta-analysis.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2016 Jun;65:142-56. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.03.026. Epub 2016 Mar 31. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2016. PMID: 27039344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Connectivity-based parcellation of the amygdala and identification of its main white matter connections.Sci Rep. 2023 Jan 24;13(1):1305. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-28100-6. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36693904 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aggleton JP. A description of intra-amygdaloid connections in Old World monkeys. Exp Brain Res. 1985;57:390–9. - PubMed
-
- Amunts K, Kedo O, Kindler M, Pieperhoff P, Mohlberg H, Shah N, et al. Cytoarchitectonic mapping of the human amygdala, hippocampal region and entorhinal cortex: Intersubject variability and probability maps. Anat Embryol. 2005;210:343–52. - PubMed
-
- Armony JL, Corbo V, Clement MH, Brunet A. Amygdala response in patients with acute PTSD to masked and unmasked emotional facial expressions. Am J Psychiatry. 2005;162:1961–3. - PubMed
-
- Bawden H, Racine R. Effects of bilateral kindling or bilateral sub-threshold stimulation of the amygdala or septum on muricide, ranacide, intraspecific aggression and passive avoidance in the rat. Phys Behav. 1979;22:115–23. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

