The efficacy and safety of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor saxagliptin in treatment-naïve patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 22828124
- PMCID: PMC3541110
- DOI: 10.1186/1758-5996-4-36
The efficacy and safety of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor saxagliptin in treatment-naïve patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to assess efficacy and safety of saxagliptin monotherapy for up to 76 weeks in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and inadequate glycemic control, with main efficacy assessment at 24 weeks.
Methods: 365 treatment-naïve patients with T2DM (HbA1c 7.0%-10.0%) were treated with saxagliptin 2.5 mg q.A.M., saxagliptin 2.5 mg q.A.M. with possible titration to saxagliptin 5 mg, saxagliptin 5 mg q.A.M., saxagliptin 5 mg q.P.M., or placebo. After week 24, patients in all groups were eligible for titration to saxagliptin 10 mg based on HbA1c ≥7%, and all unrescued placebo patients began blinded metformin 500 mg/day. Rescue with open-label metformin was available for patients with inadequate glycemic control.
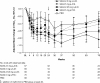
Results: At week 24, placebo-subtracted mean HbA1c reduction from baseline (LOCF) was significantly greater in the saxagliptin treatment groups vs placebo, and remained greater through week 76. Serious adverse events (AEs) and discontinuations due to AEs were similar in saxagliptin and control groups; incidence of confirmed hypoglycemia was low across all treatment groups (saxagliptin-treated, 2 [0.7]; control, 1 [1.4]).
Conclusions: In treatment-naïve patients with T2DM, saxagliptin monotherapy demonstrated statistically significant improvement in HbA1c compared with placebo at 24 weeks and was generally well tolerated for up to 76 weeks.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT00316082.
Figures

References
-
- Onglyza® (saxagliptin) Full Prescribing Information. Princeton, NJ/Wilmington, DE: Bristol-Myers Sqibb/AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP; 2009.
-
- Rosenstock J, Aguilar-Salinas C, Klein E, Nepal S, List J, Chen R. Chen R. Effect of saxagliptin monotherapy in treatment-naive patients with type 2 diabetes. Curr Med Res Opin . 2006;25:2401–11. - PubMed
-
- DeFronzo R, Hissa MN, Garber AJ, Gross JL, Duan RY, Ravichandran S, Chen R. Once-daily saxagliptin added to metformin provides sustained glycemic control and is well tolerated over 102 weeks in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2009;58:547-P.
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

