The mTOR inhibitor, everolimus (RAD001), overcomes resistance to imatinib in quiescent Ph-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells
- PMID: 22829152
- PMCID: PMC3255258
- DOI: 10.1038/bcj.2011.16
The mTOR inhibitor, everolimus (RAD001), overcomes resistance to imatinib in quiescent Ph-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells
Abstract
In Ph-positive (Ph(+)) leukemia, the quiescent cell state is one of the reasons for resistance to the BCR-ABL-kinase inhibitor, imatinib. In order to examine the mechanisms of resistance due to quiescence and the effect of the mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor, everolimus, for such a resistant population, we used Ph(+) acute lymphoblastic leukemia patient cells serially xenotransplanted into NOD/SCID/IL2rγ(null) (NOG) mice. Spleen cells from leukemic mice showed a higher percentage of slow-cycling G(0) cells in the CD34(+)CD38(-) population compared with the CD34(+)CD38(+) and CD34(-) populations. After ex vivo imatinib treatment, more residual cells were observed in the CD34(+)CD38(-) population than in the other populations. Although slow-cycling G(0) cells were insensitive to imatinib in spite of BCR-ABL and CrkL dephosphorylation, combination treatment with everolimus induced substantial cell death, including that of the CD34(+)CD38(-) population, with p70-S6 K dephosphorylation and decrease of MCL-1 expression. The leukemic non-obese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficiency (NOD/SCID) mouse system with the in vivo combination treatment with imatinib and everolimus showed a decrease of tumor burden including CD34(+) cells. These results imply that treatment with everolimus can overcome resistance to imatinib in Ph(+) leukemia due to quiescence.
Figures
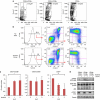
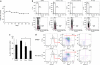


References
-
- Wassmann B, Pfeifer H, Goekbuget N, Beelen DW, Beck J, Stelljes M, et al. Alternating versus concurrent schedules of imatinib and chemotherapy as front-line therapy for Philadelphia-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph+ ALL) Blood. 2006;108:1469–1477. - PubMed
-
- Quintas-Cardama A, Kantarjian H, Cortes J. Imatinib and beyond—exploring the full potential of targeted therapy for CML. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2009;6:535–543. - PubMed
-
- Michor F, Hughes TP, Iwasa Y, Branford S, Shah NP, Sawyers CL, et al. Dynamics of chronic myeloid leukaemia. Nature. 2005;435:1267–1270. - PubMed
-
- Roeder I, Horn M, Glauche I, Hochhaus A, Mueller MC, Loeffler M. Dynamic modeling of imatinib-treated chronic myeloid leukemia: functional insights and clinical implications. Nat Med. 2006;12:1181–1184. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

