Syndrome specificity and mother-child interactions: examining positive and negative parenting across contexts and time
- PMID: 22829243
- PMCID: PMC3548024
- DOI: 10.1007/s10803-012-1605-x
Syndrome specificity and mother-child interactions: examining positive and negative parenting across contexts and time
Abstract
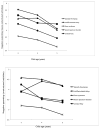
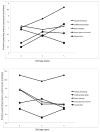
This study examined the extent to which child syndromes and observation context related to mothers' parenting behaviors. Longitudinal observations were conducted of parenting behavior across ages 3, 4, and 5 years during structured and unstructured activities. The 183 participants included mothers of children with autism spectrum disorders, cerebral palsy, Down syndrome, undifferentiated developmental delay, or typical cognitive development. Negative parenting behaviors were higher in structured activities and higher in mothers of children in all developmentally delayed groups. Positive parenting was higher in unstructured activities and especially high for mothers of children with Down syndrome. Despite differences found through direct observation of parenting children in different diagnostic groups, they are not as strong as syndrome-group differences found through more commonly used self-report questionnaires assessing domains like parenting stress.
Figures
References
-
- Aicardi J, Bax M. Cerebral palsy. In: Aicardi J, editor. Diseases of the nervous system in childhood. London: MacKeith; 1992. pp. 300–367.
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 4. Washington DC: Author; 2000. Text Revision.
-
- Aspland H, Gardner F. Observational measures of parent-child interaction: An introductory review. Child and Adolescent Mental Health. 2003;8:136–143. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

