MicroRNA signatures in B-cell lymphomas
- PMID: 22829247
- PMCID: PMC3288280
- DOI: 10.1038/bcj.2012.1
MicroRNA signatures in B-cell lymphomas
Abstract
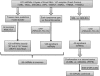
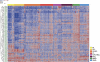
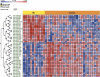
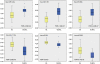
Accurate lymphoma diagnosis, prognosis and therapy still require additional markers. We explore the potential relevance of microRNA (miRNA) expression in a large series that included all major B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) types. The data generated were also used to identify miRNAs differentially expressed in Burkitt lymphoma (BL) and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) samples. A series of 147 NHL samples and 15 controls were hybridized on a human miRNA one-color platform containing probes for 470 human miRNAs. Each lymphoma type was compared against the entire set of NHLs. BL was also directly compared with DLBCL, and 43 preselected miRNAs were analyzed in a new series of routinely processed samples of 28 BLs and 43 DLBCLs using quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. A signature of 128 miRNAs enabled the characterization of lymphoma neoplasms, reflecting the lymphoma type, cell of origin and/or discrete oncogene alterations. Comparative analysis of BL and DLBCL yielded 19 differentially expressed miRNAs, which were confirmed in a second confirmation series of 71 paraffin-embedded samples. The set of differentially expressed miRNAs found here expands the range of potential diagnostic markers for lymphoma diagnosis, especially when differential diagnosis of BL and DLBCL is required.
Figures
References
-
- Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, et al. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. IARC Press: Lyon; 2008.
-
- Aggarwal M, Sanchez-Beato M, Gomez-Lopez G, Al-Shahrour F, Martinez N, Rodriguez A, et al. Functional signatures identified in B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma profiles. Leuk Lymphoma. 2009;50:1699–1708. - PubMed
-
- Hummel M, Bentink S, Berger H, Klapper W, Wessendorf S, Barth TF, et al. A biologic definition of Burkitt's lymphoma from transcriptional and genomic profiling. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:2419–2430. - PubMed
-
- Dave SS, Fu K, Wright GW, Lam LT, Kluin P, Boerma EJ, et al. Molecular diagnosis of Burkitt's lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:2431–2442. - PubMed
-
- Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature. 2005;435:834–838. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

