Hollow copper sulfide nanoparticle-mediated transdermal drug delivery
- PMID: 22829400
- PMCID: PMC3485307
- DOI: 10.1002/smll.201200783
Hollow copper sulfide nanoparticle-mediated transdermal drug delivery
Abstract
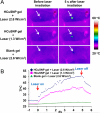
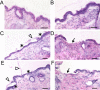
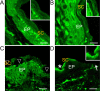
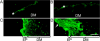
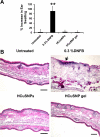
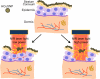
A photothermal ablation-enhanced transdermal drug delivery methodology is developed based on hollow copper sulfide nanoparticles (HCuSNPs) with intense photothermal coupling effects. Application of nanosecond-pulsed near-infrared laser allows rapid heating of the nanoparticles and instantaneous heat conduction. This provides very short periods of time but extremely high temperatures in local regions, with focused thermal ablation of the stratum corneum. The depth of skin perforations can be controlled by adjusting the laser power. Skin disruption by HCuSNP-mediated photothermal ablation significantly increases the permeability of human growth hormone. This technique offers compelling opportunities for macromolecular drug and vaccine delivery.
Copyright © 2012 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures
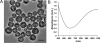
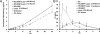
Similar articles
-
CW/pulsed NIR irradiation of gold nanorods: effect on transdermal protein delivery mediated by photothermal ablation.J Control Release. 2013 Oct 28;171(2):178-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2013.07.003. Epub 2013 Jul 14. J Control Release. 2013. PMID: 23863449
-
A comparative study of hollow copper sulfide nanoparticles and hollow gold nanospheres on degradability and toxicity.ACS Nano. 2013 Oct 22;7(10):8780-93. doi: 10.1021/nn403202w. Epub 2013 Oct 1. ACS Nano. 2013. PMID: 24053214 Free PMC article.
-
Non-ablative fractional laser assists cutaneous delivery of small- and macro-molecules with minimal bacterial infection risk.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2016 Sep 20;92:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2016.06.016. Epub 2016 Jun 21. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2016. PMID: 27345564
-
Lasers as an approach for promoting drug delivery via skin.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2014 Apr;11(4):599-614. doi: 10.1517/17425247.2014.885501. Epub 2014 Feb 3. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2014. PMID: 24490743 Review.
-
Ultrasound and transdermal drug delivery.Drug Discov Today. 2004 Aug 1;9(15):670-6. doi: 10.1016/S1359-6446(04)03170-8. Drug Discov Today. 2004. PMID: 15279850 Review.
Cited by
-
Inside-outside self-assembly of light-activated fast-release liposomes.Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2015 Jun 28;17(24):15569-78. doi: 10.1039/c4cp05881j. Epub 2015 Mar 2. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2015. PMID: 25729792 Free PMC article.
-
The combined therapeutic effects of 131iodine-labeled multifunctional copper sulfide-loaded microspheres in treating breast cancer.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2018 May;8(3):371-380. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2018.04.001. Epub 2018 Apr 7. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2018. PMID: 29881676 Free PMC article.
-
Theranostic CuS Nanoparticles Targeting Folate Receptors for PET Image-Guided Photothermal Therapy.J Mater Chem B. 2015 Dec 14;3(46):8939-8948. doi: 10.1039/C5TB01866H. Epub 2015 Oct 22. J Mater Chem B. 2015. PMID: 27725882 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements in Skin-Mediated Drug Delivery: Mechanisms, Techniques, and Applications.Adv Healthc Mater. 2024 Mar;13(7):e2302375. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202302375. Epub 2023 Dec 7. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024. PMID: 38009520 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticles for Topical Application in the Treatment of Skin Dysfunctions-An Overview of Dermo-Cosmetic and Dermatological Products.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 15;23(24):15980. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415980. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555619 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Prausnitz MR, Mitragotri S, Langer R. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004;3:115–124. - PubMed
-
- Elias PM, Choi EH. Exp. Dermatol. 2005;14:719–726. - PubMed
-
- Prausnitz MR. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004;56:581–587. - PubMed
-
- Park JH, Lee JW, Kim YC, Prausnitz MR. Int. J. Pharm. 2008;359:94–103. - PMC - PubMed
- Bramson J, Dayball K, Evelegh C, Wan YH, Page D, Smith A. Gene Ther. 2003;10:251–260. - PubMed
- Birchall J, Coulman S, Anstey A, Gateley C, Sweetland H, Gershonowitz A, Neville L, Levin G. Int. J. Pharm. 2006;312:15–23. - PubMed
- Levin G, Gershonowitz A, Sacks H, Stern M, Sherman A, Rudaev S, Zivin I, Phillip M. Pharm. Res. 2005;22:550–555. - PubMed
- Fang JY, Lee WR, Shen SC, Wang HY, Fang CL, Hu CH. J. Control. Release. 2004;100:75–85. - PubMed
- Bachhav YG, Summer S, Heinrich A, Bragagna T, Bohler C, Kalia YN. J. Control. Release. 2010;146:31–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

