A prospective study of leukocyte telomere length and risk of type 2 diabetes in postmenopausal women
- PMID: 22829448
- PMCID: PMC3478524
- DOI: 10.2337/db12-0241
A prospective study of leukocyte telomere length and risk of type 2 diabetes in postmenopausal women
Abstract
Telomere length (TL) has been implicated in the pathogenesis of age-related disorders. However, there are no prospective studies directly investigating the role of TL and relevant genes in diabetes development. In the multiethnic Women's Health Initiative, we identified 1,675 incident diabetes case participants in 6 years of follow-up and 2,382 control participants matched by age, ethnicity, clinical center, time of blood draw, and follow-up duration. Leukocyte TL at baseline was measured using quantitative PCR, and Mendelian randomization analysis was conducted to test whether TL is causally associated with diabetes risk. After adjustment for matching and known diabetes risk factors, odds ratios per 1-kilobase increment were 1.00 (95% CI 0.90-1.11) in whites, 0.95 (0.85-1.06) in blacks, 0.96 (0.79-1.17) in Hispanics, and 0.88 (0.70-1.10) in Asians. Of the 80 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in nine genes involved in telomere regulation, 14 SNPs were predictive of TL, but none were significantly associated with diabetes risk. Using ethnicity-specific SNPs as randomization instruments, we observed no statistically significant association between TL and diabetes risk (P = 0.52). Although leukocyte TL was weakly associated with diabetes risk, this association was not independent of known risk factors. These prospective findings indicate limited clinical utility of TL in diabetes risk stratification among postmenopausal women.
Figures
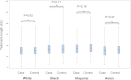
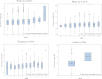
References
-
- von Zglinicki T. Role of oxidative stress in telomere length regulation and replicative senescence. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2000;908:99–110 - PubMed
-
- von Zglinicki T. Oxidative stress shortens telomeres. Trends Biochem Sci 2002;27:339–344 - PubMed
-
- Cawthon RM, Smith KR, O’Brien E, Sivatchenko A, Kerber RA. Association between telomere length in blood and mortality in people aged 60 years or older. Lancet 2003;361:393–395 - PubMed
-
- Takubo K, Izumiyama-Shimomura N, Honma N, et al. Telomere lengths are characteristic in each human individual. Exp Gerontol 2002;37:523–531 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01-WH-32115/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-32113/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-42110/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- R21-DK-084452/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-42132/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-42111/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK084452/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-42119/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-44221/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-42112/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-32119/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-42117/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-32112/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-32118/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-42114/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-32105/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-42125/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-42126/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-32102/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-42120/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 WH022110/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-42131/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-42121/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-42115/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-42113/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-42124/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-42107/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-42116/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-42109/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-32101/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-32108/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-42130/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-32111/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-42122/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-32106/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-32122/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-32100/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-42123/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-42108/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-22110/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-24152/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-42129/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-42118/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-WH-32109/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States

