Histone H2B monoubiquitination facilitates the rapid modulation of gene expression during Arabidopsis photomorphogenesis
- PMID: 22829781
- PMCID: PMC3400566
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002825
Histone H2B monoubiquitination facilitates the rapid modulation of gene expression during Arabidopsis photomorphogenesis
Abstract
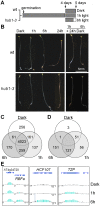
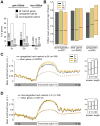
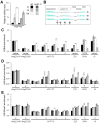
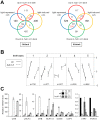
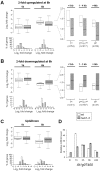
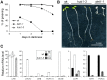
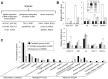
Profiling of DNA and histone modifications has recently allowed the establishment of reference epigenomes from several model organisms. This identified a major chromatin state for active genes that contains monoubiquitinated H2B (H2Bub), a mark linked to transcription elongation. However, assessment of dynamic chromatin changes during the reprogramming of gene expression in response to extrinsic or developmental signals has been more difficult. Here we used the major developmental switch that Arabidopsis thaliana plants undergo upon their initial perception of light, known as photomorphogenesis, as a paradigm to assess spatial and temporal dynamics of monoubiquitinated H2B (H2Bub) and its impact on transcriptional responses. The process involves rapid and extensive transcriptional reprogramming and represents a developmental window well suited to studying cell division-independent chromatin changes. Genome-wide H2Bub distribution was determined together with transcriptome profiles at three time points during early photomorphogenesis. This revealed de novo marking of 177 genes upon the first hour of illumination, illustrating the dynamic nature of H2Bub enrichment in a genomic context. Gene upregulation was associated with H2Bub enrichment, while H2Bub levels generally remained stable during gene downregulation. We further report that H2Bub influences the modulation of gene expression, as both gene up- and downregulation were globally weaker in hub1 mutant plants that lack H2Bub. H2Bub-dependent regulation notably impacted genes with fast and transient light induction, and several circadian clock components whose mRNA levels are tightly regulated by sharp oscillations. Based on these findings, we propose that H2B monoubiquitination is part of a transcription-coupled, chromatin-based mechanism to rapidly modulate gene expression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Baker M. Making sense of chromatin states. Nat Methods. 2011;8:717–722. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

