Recent Insights into Antibiotic Resistance in Helicobacter pylori Eradication
- PMID: 22829809
- PMCID: PMC3398622
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/723183
Recent Insights into Antibiotic Resistance in Helicobacter pylori Eradication
Abstract
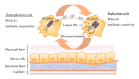
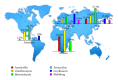
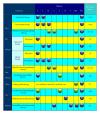
Antibiotics have been useful in the treatment of H. pylori-related benign and malignant gastroduodenal diseases. However, emergence of antibiotic resistance often decreases the eradication rates of H. pylori infections. Many factors have been implicated as causes of treatment failure, but the main antibiotic resistance mechanisms described to date are due to point mutations on the bacterial chromosome, a consequence of a significantly phenotypic variation in H. pylori. The prevalence of antibiotic (e.g., clarithromycin, metronidazole, tetracycline, amoxicillin, and furazolidone) resistance varies among different countries; it appears to be partly determined by geographical factors. Since the worldwide increase in the rate of antibiotic resistance represents a problem of relevance, some studies have been performed in order to identify highly active and well-tolerated anti-H. pylori therapies including sequential, concomitant quadruple, hybrid, and quadruple therapy. These represent a promising alternatives in the effort to overcome the problem of resistance. The aim of this paper is to review the current status of antibiotic resistance in H. pylori eradication, highlighting the evolutionary processes in detail at alternative approaches to treatment in the past decade. The underlying resistance mechanisms will be also followed.
Figures
References
-
- Necchi V, Candusso ME, Tava F, et al. Intracellular, intercellular, and stromal invasion of gastric mucosa, preneoplastic lesions, and cancer byHelicobacter pylori . Gastroenterology. 2007;132(3):1009–1023. - PubMed
-
- Friedrich MJ. Microbiome project seeks to understand human body’s microscopic residents. JAMA. 2008;300(7):777–778. - PubMed
-
- Graham DY, Fischbach L. Helicobacter pylori treatment in the era of increasing antibiotic resistance. Gut. 2010;59(8):1143–1153. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

