Double allogenic mesenchymal stem cells transplantations could not enhance therapeutic effect compared with single transplantation in systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 22829849
- PMCID: PMC3399403
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/273291
Double allogenic mesenchymal stem cells transplantations could not enhance therapeutic effect compared with single transplantation in systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
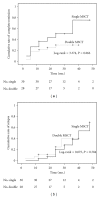
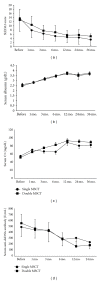
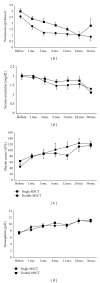
The clinical trial of allogenic mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) transplantation for refractory SLE patients has shown significant safety and efficacy profiles. However, the optimum frequency of the MSCs transplantation (MSCT) is unknown. This study was undertaken to observe whether double transplantations of MSCs is superior to single transplantation. Fifty-eight refractory SLE patients were enrolled in this study, in which 30 were randomly given single MSCT, and the other 28 were given double MSCT. Patients were followed up for rates of survival, disease remission, and relapse, as well as transplantation-related adverse events. SLE disease activity index (SLEDAI) and serologic features were evaluated. Our results showed that no remarkable differences between single and double allogenic MSCT were found in terms of disease remission and relapse, amelioration of disease activity, and serum indexes in an SLE clinical trial with more than one year followup. This study demonstrated that single MSCs transplantation at the dose of one million MSCs per kilogram of body weight was sufficient to induce disease remission for refractory SLE patients.
Figures
References
-
- Houssiau FA, Ginzler EM. Current treatment of lupus nephritis. Lupus. 2008;17(5):426–430. - PubMed
-
- Karim MY, Pisoni CN, Khamashta MA. Update on immunotherapy for systemic lupus erythematosus - What’s hot and what’s not! Rheumatology. 2009;48(4):332–341. - PubMed
-
- Nauta AJ, Fibbe WE. Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stromal cells. Blood. 2007;110(10):3499–3506. - PubMed
-
- Singer NG, Caplan AI. Mesenchymal stem cells: mechanisms of inflammation. Annual Review of Pathology: Mechanisms of Disease. 2011;6:457–478. - PubMed
-
- Hoogduijn MJ, Popp F, Verbeek R, et al. The immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells and their use for immunotherapy. International Immunopharmacology. 2010;10(12):1496–1500. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

