Deciphering the role of insulin-like growth factor-I receptor in trastuzumab resistance
- PMID: 22830017
- PMCID: PMC3399380
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/648965
Deciphering the role of insulin-like growth factor-I receptor in trastuzumab resistance
Abstract
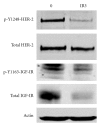
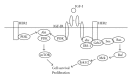
Resistance to the HER2-targeted antibody trastuzumab is a major clinical concern in the treatment of HER2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer. Increased expression or signaling of the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor (IGF-IR) has been reported in a subset of cell lines and clinical samples derived from trastuzumab-resistant breast cancers. Genetic and pharmacologic inhibition of IGF-IR signaling has been shown to improve response to trastuzumab in trastuzumab-naïve and trastuzumab-resistant models. In this paper, we will discuss the role of IGF-IR signaling in trastuzumab resistance. Further, we will discuss cotargeting IGF-IR and HER2 as a potential therapeutic strategy for HER2-over-expressing breast cancers that have progressed on trastuzumab treatment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Superior antitumor activity of a novel bispecific antibody cotargeting human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 and type I insulin-like growth factor receptor.Mol Cancer Ther. 2014 Jan;13(1):90-100. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0558. Epub 2013 Nov 13. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014. PMID: 24227890
-
Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 heterodimerization contributes to trastuzumab resistance of breast cancer cells.Cancer Res. 2005 Dec 1;65(23):11118-28. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-3841. Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16322262
-
Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling and resistance to trastuzumab (Herceptin).J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001 Dec 19;93(24):1852-7. doi: 10.1093/jnci/93.24.1852. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001. PMID: 11752009
-
Cross-talk between the ErbB/HER family and the type I insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway in breast cancer.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2008 Dec;13(4):485-98. doi: 10.1007/s10911-008-9107-3. Epub 2008 Nov 25. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2008. PMID: 19034632 Review.
-
Evolving strategies for overcoming resistance to HER2-directed therapy: targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway.Clin Breast Cancer. 2010 Nov;10 Suppl 3:S72-8. doi: 10.3816/CBC.2010.s.015. Clin Breast Cancer. 2010. PMID: 21115425 Review.
Cited by
-
Lack of interaction between ErbB2 and insulin receptor substrate signaling in breast cancer.Cell Commun Signal. 2016 Oct 21;14(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s12964-016-0148-8. Cell Commun Signal. 2016. PMID: 27765041 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of IGF-1R expression on the outcomes of patients with breast cancer: a meta-analysis.Onco Targets Ther. 2015 Jan 29;8:279-87. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S74774. eCollection 2015. Onco Targets Ther. 2015. PMID: 25674003 Free PMC article.
-
Role of IGF1R in Breast Cancer Subtypes, Stemness, and Lineage Differentiation.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2015 Apr 24;6:59. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2015.00059. eCollection 2015. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2015. PMID: 25964777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential expression of the insulin-like growth factor receptor among early breast cancer subtypes.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 17;9(3):e91407. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091407. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24637962 Free PMC article.
-
Association of insulin-like growth factor-I receptor polymorphism with colorectal cancer development.Mol Biol Rep. 2014 Dec;41(12):8099-106. doi: 10.1007/s11033-014-3708-2. Epub 2014 Sep 5. Mol Biol Rep. 2014. PMID: 25189651
References
-
- Slamon DJ, Clark GM, Wong SG, Levin WJ, Ullrich A, McGuire WL. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science. 1987;235(4785):177–182. - PubMed
-
- Baselga J, Tripathy D, Mendelsohn J, et al. Phase II study of weekly intravenous recombinant humanized anti-p185HER2 monoclonal antibody in patients with HER2/neu-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 1996;14(3):737–744. - PubMed
-
- Cobleigh MA, Vogel CL, Tripathy D, et al. Multinational study of the efficacy and safety of humanized anti-HER2 monoclonal antibody in women who have HER2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer that has progressed after chemotherapy for metastatic disease. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 1999;17(9):2639–2648. - PubMed
-
- Esteva FJ, Valero V, Booser D, et al. Phase II study of weekly docetaxel and trastuzumab for patients with HER-2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2002;20(7):1800–1808. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
