Hippo and rassf1a Pathways: A Growing Affair
- PMID: 22830020
- PMCID: PMC3399428
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/307628
Hippo and rassf1a Pathways: A Growing Affair
Abstract
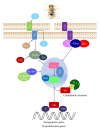
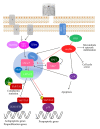
First discovered in Drosophila, the Hippo pathway regulates the size and shape of organ development. Its discovery and study have helped to address longstanding questions in developmental biology. Central to this pathway is a kinase cascade leading from the tumor suppressor Hippo (Mst1 and Mst2 in mammals) to the Yki protein (YAP and TAZ in mammals), a transcriptional coactivator of target genes involved in cell proliferation, survival, and apoptosis. A dysfunction of the Hippo pathway activity is frequently detected in human cancers. Recent studies have highlighted that the Hippo pathway may play an important role in tissue homoeostasis through the regulation of stem cells, cell differentiation, and tissue regeneration. Recently, the impact of RASSF proteins on Hippo signaling potentiating its proapoptotic activity has been addressed, thus, providing further evidence for Hippo's key role in mammalian tumorigenesis as well as other important diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hippo-Independent Regulation of Yki/Yap/Taz: A Non-canonical View.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Apr 1;9:658481. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.658481. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33869224 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein kinases of the Hippo pathway: regulation and substrates.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2012 Sep;23(7):770-84. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2012.07.002. Epub 2012 Aug 9. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2012. PMID: 22898666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hippo-YAP/TAZ signaling in breast cancer: Reciprocal regulation of microRNAs and implications in precision medicine.Genes Dis. 2023 Mar 23;11(2):760-771. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2023.01.017. eCollection 2024 Mar. Genes Dis. 2023. PMID: 37692482 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mst1 and Mst2 kinases: regulations and diseases.Cell Biosci. 2013 Aug 28;3(1):31. doi: 10.1186/2045-3701-3-31. Cell Biosci. 2013. PMID: 23985272 Free PMC article.
-
Hippo Signaling in Cancer: Lessons From Drosophila Models.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019 May 24;7:85. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2019.00085. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 31231648 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The RASSF1A Tumor Suppressor Binds the RasGAP DAB2IP and Modulates RAS Activation in Lung Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Dec 17;12(12):3807. doi: 10.3390/cancers12123807. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33348649 Free PMC article.
-
The tumor suppressor gene, RASSF1A, is essential for protection against inflammation -induced injury.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 16;8(10):e75483. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075483. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24146755 Free PMC article.
-
RASSF1A inhibits PDGFB-driven malignant phenotypes of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells in a YAP1-dependent manner.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Oct 14;11(10):855. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03054-z. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 33057010 Free PMC article.
-
The YAP/TAZ Pathway in Osteogenesis and Bone Sarcoma Pathogenesis.Cells. 2020 Apr 15;9(4):972. doi: 10.3390/cells9040972. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32326412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The OncoPPi network of cancer-focused protein-protein interactions to inform biological insights and therapeutic strategies.Nat Commun. 2017 Feb 16;8:14356. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14356. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28205554 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Justice RW, Zilian O, Woods DF, Noll M, Bryant PJ. The Drosophila tumor suppressor gene warts encodes a homolog of human myotonic dystrophy kinase and is required for the control of cell shape and proliferation. Genes and Development. 1995;9(5):534–546. - PubMed
-
- Tapon N, Harvey KF, Bell DW, et al. salvador promotes both cell cycle exit and apoptosis in Drosophila and is mutated in human cancer cell lines. Cell. 2002;110(4):467–478. - PubMed
-
- Wu S, Huang J, Dong J, Pan D. hippo encodes a Ste-20 family protein kinase that restricts cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis in conjunction with salvador and warts. Cell. 2003;114(4):445–456. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
