A Model of Left Ventricular Dysfunction Complicated by CAWS Arteritis in DBA/2 Mice
- PMID: 22830029
- PMCID: PMC3399367
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/570297
A Model of Left Ventricular Dysfunction Complicated by CAWS Arteritis in DBA/2 Mice
Abstract
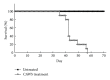
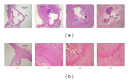
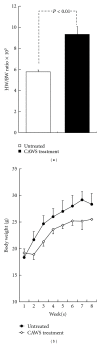
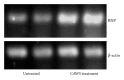
It was reported previously that a Candida albicans water-soluble fraction (CAWS), including a mannoprotein and β-glucan complex, has strong potency in inducing fatal necrotizing arteritis in DBA/2 mice. In this study, histopathological changes and cardiac function were investigated in this system. One mg/day of CAWS was given to DBA/2 mice via peritoneal injection for five days. The CAWS-treated DBA/2 mice were induced aortitis and died at an incidence of 100% within several weeks. Histological findings included stenosis in the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) and severe inflammatory changes of the aortic valve with fibrinoid necrosis. Cardiomegaly was observed and heart weight increased 1.62 fold (P < 0.01). Echocardiography revealed a severe reduction in contractility and dilatation of the cavity in the left ventricle (LV): LV fractional shortening (LVFS) decreased from 71% to 38% (P < 0.01), and the LV end-diastolic diameter (LVDd) increased from 2.21 mm to 3.26 mm (P < 0.01). The titer of BNP mRNA increased in the CAWS-treated group. Severe inflammatory changes resulting from CAWS brought about lethal LV dysfunction by aortic valve deformation with LVOT stenosis. This system is proposed as an easy and useful experimental model of heart failure because CAWS arteritis can be induced by CAWS injection alone.
Figures




References
-
- Nürnberger T, Brunner F, Kemmerling B, Piater L. Innate immunity in plants and animals: striking similarities and obvious differences. Immunological Reviews. 2004;198:249–266. - PubMed
-
- Ohno N. Chemistry and biology of angiitis inducer, Candida albicans water-soluble mannoprotein-β-glucan complex (CAWS) Microbiology and Immunology. 2003;47(7):479–490. - PubMed
-
- Ohno N. A murine model of vasculitis induced by fungal polysaccharide. Cardiovascular and Hematological Agents in Medicinal Chemistry. 2008;6(1):44–52. - PubMed
-
- Nagi-Miura N, Harada T, Shinohara H, et al. Lethal and severe coronary arteritis in DBA/2 mice induced by fungal pathogen, CAWS, Candida albicans water-soluble fraction. Atherosclerosis. 2006;186(2):310–320. - PubMed
-
- Nagi-Miura N, Shingo Y, Adachi Y, et al. Induction of coronary arteritis with administration of CAWS (Candida albicans water-soluble fraction) depending on mouse strains. Immunopharmacology and Immunotoxicology. 2004;26(4):527–543. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

