Drug solubility: importance and enhancement techniques
- PMID: 22830056
- PMCID: PMC3399483
- DOI: 10.5402/2012/195727
Drug solubility: importance and enhancement techniques
Abstract
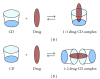
Solubility, the phenomenon of dissolution of solute in solvent to give a homogenous system, is one of the important parameters to achieve desired concentration of drug in systemic circulation for desired (anticipated) pharmacological response. Low aqueous solubility is the major problem encountered with formulation development of new chemical entities as well as for the generic development. More than 40% NCEs (new chemical entities) developed in pharmaceutical industry are practically insoluble in water. Solubility is a major challenge for formulation scientist. Any drug to be absorbed must be present in the form of solution at the site of absorption. Various techniques are used for the enhancement of the solubility of poorly soluble drugs which include physical and chemical modifications of drug and other methods like particle size reduction, crystal engineering, salt formation, solid dispersion, use of surfactant, complexation, and so forth. Selection of solubility improving method depends on drug property, site of absorption, and required dosage form characteristics.
Figures
References
-
- Lachman L, Lieberman H, Kanig JL. The Theory And Practise of Industrial Pharmacy. 3rd edition. Lea & Febiger; 1986.
-
- Clugston M, Fleming R. Advanced Chemistry. 1st edition. Oxford, UK: Oxford Publishing; 2000.
-
- Myrdal PB, Yalkowsky SH. Solubilization of drugs in aqueous media. In: Swarbrick J, editor. Encyclopedia of Pharmaceutical Technology. 3rd edition. New York, NY, USA, : Informa Health Care; 2007. p. p. 3311.
-
- Martin A. Solubility and Distribution Phenomena. 6th edition. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2011. (Physical Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences).
-
- IUPAC gold book. http://goldbook.iupac.org/S05740.html.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources