Assembly and regulation of the membrane attack complex based on structures of C5b6 and sC5b9
- PMID: 22832194
- PMCID: PMC3314296
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2012.02.003
Assembly and regulation of the membrane attack complex based on structures of C5b6 and sC5b9
Abstract
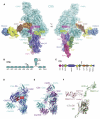
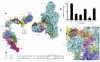
Activation of the complement system results in formation of membrane attack complexes (MACs), pores that disrupt lipid bilayers and lyse bacteria and other pathogens. Here, we present the crystal structure of the first assembly intermediate, C5b6, together with a cryo-electron microscopy reconstruction of a soluble, regulated form of the pore, sC5b9. Cleavage of C5 to C5b results in marked conformational changes, distinct from those observed in the homologous C3-to-C3b transition. C6 captures this conformation, which is preserved in the larger sC5b9 assembly. Together with antibody labeling, these structures reveal that complement components associate through sideways alignment of the central MAC-perforin (MACPF) domains, resulting in a C5b6-C7-C8β-C8α-C9 arc. Soluble regulatory proteins below the arc indicate a potential dual mechanism in protection from pore formation. These results provide a structural framework for understanding MAC pore formation and regulation, processes important for fighting infections and preventing complement-mediated tissue damage.
Copyright © 2012 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Structure of complement C6 suggests a mechanism for initiation and unidirectional, sequential assembly of membrane attack complex (MAC).J Biol Chem. 2012 Mar 23;287(13):10210-10222. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.327809. Epub 2012 Jan 20. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22267737 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of C5b-6 suggests structural basis for priming assembly of the membrane attack complex.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jun 1;287(23):19642-52. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.361121. Epub 2012 Apr 12. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22500023 Free PMC article.
-
CryoEM reveals how the complement membrane attack complex ruptures lipid bilayers.Nat Commun. 2018 Dec 14;9(1):5316. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07653-5. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30552328 Free PMC article.
-
Structural biology of the membrane attack complex.Subcell Biochem. 2014;80:83-116. doi: 10.1007/978-94-017-8881-6_6. Subcell Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24798009 Review.
-
Cholesterol-dependent cytolysins.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;677:56-66. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-6327-7_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 20687480 Review.
Cited by
-
The Apicomplexan CDC/MACPF-like pore-forming proteins.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2015 Aug;26:48-52. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2015.05.001. Epub 2015 May 27. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26025132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Incomplete pneumolysin oligomers form membrane pores.Open Biol. 2014 Apr 23;4(4):140044. doi: 10.1098/rsob.140044. Open Biol. 2014. PMID: 24759615 Free PMC article.
-
Expanding horizons in complement drug discovery: challenges and emerging strategies.Semin Immunopathol. 2018 Jan;40(1):125-140. doi: 10.1007/s00281-017-0655-8. Epub 2017 Oct 6. Semin Immunopathol. 2018. PMID: 28986638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional analysis of a complement polymorphism (rs17611) associated with rheumatoid arthritis.J Immunol. 2015 Apr 1;194(7):3029-34. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1402956. Epub 2015 Feb 27. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25725109 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the poly-C9 component of the complement membrane attack complex.Nat Commun. 2016 Feb 4;7:10588. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10588. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 26841934 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blanc E, Roversi P, Vonrhein C, Flensburg C, Lea SM, Bricogne G. Refinement of severely incomplete structures with maximum likelihood in BUSTER-TNT. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2004;60:2210–2221. - PubMed
-
- Botto M, Kirschfink M, Macor P, Pickering MC, Würzner R, Tedesco F. Complement in human diseases: Lessons from complement deficiencies. Mol. Immunol. 2009;46:2774–2783. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

