Convergent functional genomic studies of ω-3 fatty acids in stress reactivity, bipolar disorder and alcoholism
- PMID: 22832392
- PMCID: PMC3309466
- DOI: 10.1038/tp.2011.1
Convergent functional genomic studies of ω-3 fatty acids in stress reactivity, bipolar disorder and alcoholism
Abstract
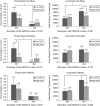
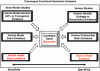
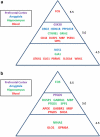
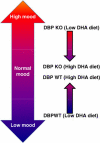
Omega-3 fatty acids have been proposed as an adjuvant treatment option in psychiatric disorders. Given their other health benefits and their relative lack of toxicity, teratogenicity and side effects, they may be particularly useful in children and in females of child-bearing age, especially during pregnancy and postpartum. A comprehensive mechanistic understanding of their effects is needed. Here we report translational studies demonstrating the phenotypic normalization and gene expression effects of dietary omega-3 fatty acids, specifically docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), in a stress-reactive knockout mouse model of bipolar disorder and co-morbid alcoholism, using a bioinformatic convergent functional genomics approach integrating animal model and human data to prioritize disease-relevant genes. Additionally, to validate at a behavioral level the novel observed effects on decreasing alcohol consumption, we also tested the effects of DHA in an independent animal model, alcohol-preferring (P) rats, a well-established animal model of alcoholism. Our studies uncover sex differences, brain region-specific effects and blood biomarkers that may underpin the effects of DHA. Of note, DHA modulates some of the same genes targeted by current psychotropic medications, as well as increases myelin-related gene expression. Myelin-related gene expression decrease is a common, if nonspecific, denominator of neuropsychiatric disorders. In conclusion, our work supports the potential utility of omega-3 fatty acids, specifically DHA, for a spectrum of psychiatric disorders such as stress disorders, bipolar disorder, alcoholism and beyond.
Figures


References
-
- Cunnane SC, Crawford MA. Survival of the fattest: fat babies were the key to evolution of the large human brain. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2003;136:17–26. - PubMed
-
- Simopoulos AP. Evolutionary aspects of diet, the omega-6/omega-3 ratio and genetic variation: nutritional implications for chronic diseases. Biomed Pharmacother. 2006;60:502–507. - PubMed
-
- DeMar JC, Jr, Ma K, Bell JM, Igarashi M, Greenstein D, Rapoport SI. One generation of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid deprivation increases depression and aggression test scores in rats. J Lipid Res. 2006;47:172–180. - PubMed
-
- Rao JS, Ertley RN, Lee HJ, DeMar JC, Jr, Arnold JT, Rapoport SI, et al. n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid deprivation in rats decreases frontal cortex BDNF via a p38 MAPK-dependent mechanism. Mol Psychiatry. 2007;12:36–46. - PubMed
-
- Zanarini MC, Frankenburg FR. Omega-3 Fatty acid treatment of women with borderline personality disorder: a double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study. Am J Psychiatry. 2003;160:167–169. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

