Postnatal emergence of serotonin-induced plateau potentials in commissural interneurons of the mouse spinal cord
- PMID: 22832564
- PMCID: PMC3545016
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00336.2012
Postnatal emergence of serotonin-induced plateau potentials in commissural interneurons of the mouse spinal cord
Abstract
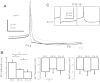
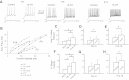
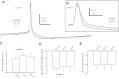
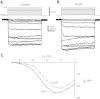
Most studies of the mouse hindlimb locomotor network have used neonatal (P0-5) mice. In this study, we examine the postnatal development of intrinsic properties and serotonergic modulation of intersegmental commissural interneurons (CINs) from the neonatal period (P0-3) to the time the animals bear weight (P8-10) and begin to show adult walking (P14-16). CINs show an increase in excitability with age, associated with a decrease in action potential halfwidth and appearance of a fast component to the afterhyperpolarization at P14-16. Serotonin (5-HT) depolarizes and increases the excitability of most CINs at all ages. The major developmental difference is that serotonin can induce plateau potential capability in P14-16 CINs, but not at younger ages. These plateau potentials are abolished by nifedipine, suggesting that they are mediated by an L-type calcium current, I(Ca(L)). Voltage-clamp analysis demonstrates that 5-HT increases a nifedipine-sensitive voltage-activated calcium current, I(Ca(V)), in P14-16 CINs but does not increase I(Ca(V)) in P8-10 CINs. These results, together with earlier work on 5-HT effects on neonatal CINs, suggest that 5-HT increases the excitability of CINs at all ages studied, but by opposite effects on calcium currents, decreasing N- and P/Q-type calcium currents and, indirectly, calcium-activated potassium current, at P0-3 but increasing I(Ca(L)) at P14-16.
Figures


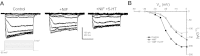

References
-
- Ballion B, Branchereau P, Chapron J, Viala D. Ontogeny of descending serotonergic innervation and evidence for intraspinal 5-HT neurons in the mouse spinal cord. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 137: 81–88, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Bennett DJ, Li Y, Siu M. Plateau potentials in sacrocaudal motoneurons of chronic spinal rats, recorded in vitro. J Neurophysiol 86: 1955–1971, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Birinyi A, Viszokay K, Weber I, Kiehn O, Antal M. Synaptic targets of commissural interneurons in the lumbar spinal cord of neonatal rats. J Comp Neurol 461: 429–440, 2003 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

