Interactions of human truncated DISC1 proteins: implications for schizophrenia
- PMID: 22832604
- PMCID: PMC3309510
- DOI: 10.1038/tp.2011.31
Interactions of human truncated DISC1 proteins: implications for schizophrenia
Abstract
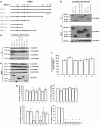
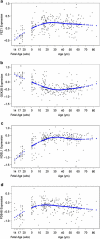
Numerous genetic linkage and association reports have implicated the Disrupted-in-Schizophrenia (DISC1) gene in psychiatric illness. The Scottish family translocation, predicted to encode a C-terminus-truncated protein, suggests involvement of short isoforms in the pathophysiology of mental disorders. We recently reported complex alternative splicing patterns for the DISC1 gene and found that short isoforms are overexpressed in the brains of patients with schizophrenia and in carriers of risk-associated alleles. Investigation into the protein-protein interactions of alternative DISC1 isoforms may provide information about the functional consequences of overexpression of truncated forms in mental illness. Human embryonic kidney (HEK293) cells were transiently co-transfected with human epitope-tagged DISC1 variants and epitope-tagged NDEL1, FEZ1, GSK3β and PDE4B constructs. Co-immunoprecipitation assays demonstrated that all truncated DISC1 variants formed complexes with full-length DISC1. Short DISC1 splice variants LΔ78, LΔ3 and Esv1 showed reduced or no binding to NDEL1 and PDE4B proteins, but fully interacted with FEZ1 and GSK3β. The temporal expression pattern of GSK3β in the human postmortem tissue across the lifespan closely resembled that of the truncated DISC1 variants, suggesting the possibility of interactions between these proteins in the human brain. Our results suggest that complexes of full-length DISC1 with truncated DISC1 variants may result in cellular disturbances critical to DISC1 function.
Figures
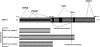
Similar articles
-
Genetic association and post-mortem brain mRNA analysis of DISC1 and related genes in schizophrenia.Schizophr Res. 2009 Oct;114(1-3):39-49. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2009.06.019. Epub 2009 Jul 24. Schizophr Res. 2009. PMID: 19632097
-
Disrupted in schizophrenia 1 and phosphodiesterase 4B: towards an understanding of psychiatric illness.J Physiol. 2007 Oct 15;584(Pt 2):401-5. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.140210. Epub 2007 Sep 6. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17823207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synergistic interactions between PDE4B and GSK-3: DISC1 mutant mice.Neuropharmacology. 2012 Mar;62(3):1252-62. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.02.020. Epub 2011 Mar 2. Neuropharmacology. 2012. PMID: 21376063
-
Expression of DISC1 binding partners is reduced in schizophrenia and associated with DISC1 SNPs.Hum Mol Genet. 2006 Apr 15;15(8):1245-58. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddl040. Epub 2006 Mar 1. Hum Mol Genet. 2006. PMID: 16510495
-
Role of DISC1 in neural development and schizophrenia.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2007 Feb;17(1):95-102. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2007.01.007. Epub 2007 Jan 26. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2007. PMID: 17258902 Review.
Cited by
-
Disrupted in schizophrenia 1 (DISC1) is a constituent of the mammalian mitochondrial contact site and cristae organizing system (MICOS) complex, and is essential for oxidative phosphorylation.Hum Mol Genet. 2016 Oct 1;25(19):4157-4169. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddw250. Epub 2016 Jul 27. Hum Mol Genet. 2016. PMID: 27466199 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond the brain: disrupted in schizophrenia 1 regulates pancreatic β-cell function via glycogen synthase kinase-3β.FASEB J. 2016 Feb;30(2):983-93. doi: 10.1096/fj.15-279810. Epub 2015 Nov 6. FASEB J. 2016. PMID: 26546129 Free PMC article.
-
DISC1 and reelin interact to alter cognition, inhibition, and neurogenesis in a novel mouse model of schizophrenia.Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 Jan 12;17:1321632. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1321632. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38283751 Free PMC article.
-
An alternative splicing hypothesis for neuropathology of schizophrenia: evidence from studies on historical candidate genes and multi-omics data.Mol Psychiatry. 2022 Jan;27(1):95-112. doi: 10.1038/s41380-021-01037-w. Epub 2021 Mar 8. Mol Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 33686213 Review.
-
Hidden in the white matter: Current views on interstitial white matter neurons.Neuroscientist. 2025 Aug;31(4):381-408. doi: 10.1177/10738584241282969. Epub 2024 Oct 4. Neuroscientist. 2025. PMID: 39365761 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chubb JE, Bradshaw NJ, Soares DC, Porteous DJ, Millar JK. The DISC locus in psychiatric illness. Mol Psychiatry. 2008;13:36–64. - PubMed
-
- Morris JA, Kandpal G, Ma L, Austin CP. DISC1 (Disrupted-in-Schizophrenia-1) is a centrosome-associated protein that interacts with MAP1A, MIPT, ATF4/5, and NUDEL: Regulations and loss of interaction with mutation. Human Molec Genetics. 2003;12:1591–1608. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

