Association of two independent functional risk haplotypes in TNIP1 with systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 22833143
- PMCID: PMC3485412
- DOI: 10.1002/art.34642
Association of two independent functional risk haplotypes in TNIP1 with systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
Objective: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease characterized by autoantibody production and altered type I interferon expression. Genetic surveys and genome-wide association studies have identified >30 SLE susceptibility genes. One of these genes, TNIP1, encodes the ABIN1 protein. ABIN1 functions in the immune system by restricting NF-κB signaling. The present study was undertaken to investigate the genetic factors that influence association with SLE in genes that regulate the NF-κB pathway.
Methods: We analyzed a dense set of genetic markers spanning TNIP1 and TAX1BP1, as well as the TNIP1 homolog TNIP2, in case-control populations of diverse ethnic origins. TNIP1, TNIP2, and TAX1BP1 were fine-mapped in a total of 8,372 SLE cases and 7,492 healthy controls from European-ancestry, African American, Hispanic, East Asian, and African American Gullah populations. Levels of TNIP1 messenger RNA (mRNA) and ABIN1 protein in Epstein-Barr virus-transformed human B cell lines were analyzed by quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and Western blotting, respectively.
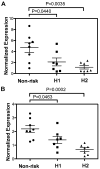
Results: We found significant associations between SLE and genetic variants within TNIP1, but not in TNIP2 or TAX1BP1. After resequencing and imputation, we identified 2 independent risk haplotypes within TNIP1 in individuals of European ancestry that were also present in African American and Hispanic populations. Levels of TNIP1 mRNA and ABIN1 protein were reduced among subjects with these haplotypes, suggesting that they harbor hypomorphic functional variants that influence susceptibility to SLE by restricting ABIN1 expression.
Conclusion: Our results confirm the association signals between SLE and TNIP1 variants in multiple populations and provide new insight into the mechanism by which TNIP1 variants may contribute to SLE pathogenesis.
Copyright © 2012 by the American College of Rheumatology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Li Q, Verma IM. NF-kappaB regulation in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2(10):725–34. - PubMed
-
- Heyninck K, Beyaert R. The cytokine-inducible zinc finger protein A20 inhibits IL-1-induced NF-kappaB activation at the level of TRAF6. FEBS Lett. 1999;442(2–3):147–50. - PubMed
-
- Wertz IE, O’Rourke KM, Zhou H, Eby M, Aravind L, Seshagiri S, et al. De-ubiquitination and ubiquitin ligase domains of A20 downregulate NF-kappaB signalling. Nature. 2004;430(7000):694–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR000154/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025777/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024148/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AR053308/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE018209/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI063274/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000079/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI082714/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P60-AR-049459/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR020143/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000150/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- RC2-AR-058959/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K24-AR-002138/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AR-042460/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM103456/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DE-018209/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AR-043274/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01-AR-62277/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024999/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 AR058554/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR053483/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P20-GM-103456/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37-24717/PHS HHS/United States
- K08 AI083790/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA-141700/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30-RR-031152/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-AI-50026/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P60-AR-053308/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-024999/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 RR031152/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-029882/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025741/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL-1RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P20-RR-020143/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K08-AI-083790/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5UL1-RR-025777/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AI-070983/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AR062277/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR056360/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 AR058621/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AI-071651/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01-AR-49084/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI070983/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR048311/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA046934/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR043814/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- 1U54-RR-23417-01/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AR049459/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR042460/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- ULI-RR-025014-02/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR057172/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AI-063274/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR033062/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR-00079/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025014/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR029882/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- L30 AI071651/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AR-043727/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AR-051545-01A2/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR043727/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- ARC_/Arthritis Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 CA141700/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-025741/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P60 2-AR-30692/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AR-33062/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR063124/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI078004/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AR002138/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01-AR-056360/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AR-43727/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30-AR-053483/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30-AR-48311/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI070304/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 AR058959/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI083194/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AR030692/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- RC1-AR-058621/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AR-43814/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AR049084/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR051545/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR043274/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21-AI-070304/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AR062755/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AI050026/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19-AI-082714/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01-AI-083194/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RC1-AR-058554/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000371/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States

