Vascular endothelial growth factor signaling in acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 22833169
- PMCID: PMC11113417
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-012-1085-3
Vascular endothelial growth factor signaling in acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
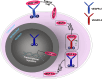
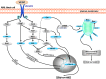
This review is designed to provide an overview of the current literature concerning vascular endothelial growth factor signaling (VEGF) in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Aberrant VEGF signaling operates in the bone marrow of AML patients and is related to a poor prognosis. The altered signaling pathway demonstrated to interfere in several autocrine and paracrine signaling pathways. VEGF signaling promotes autocrine AML blast cell proliferation, survival, and chemotherapy resistance. In addition, VEGF signaling can mediate paracrine vascular endothelial cell-controlled angiogenesis in AML. Both effects presumably explain the association of high VEGF levels and poor therapeutic outcome. More recently, researches focusing on bone marrow stem cell niches demonstrate a role for VEGF signaling in the preservation of several cell types within these niches. The bone marrow niches are proposed to be a protective microenvironment for AML cells that could be responsible for relapses in AML patients. This implies the need of sophisticated VEGF-targeted therapeutics in AML therapy strategies. This review highlights our current understanding of aberrant VEGF signaling in AML, appoints the interference of VEGF signaling in the AML-associated microenvironment, and reflects the novelty of current VEGF-targeted therapeutics used in clinical trails for the treatment of AML.
Conflict of interest statement
No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article. The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Coculture in vitro with endothelial cells induces cytarabine resistance of acute myeloid leukemia cells in a VEGF-A/VEGFR-2 signaling-independent manner.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022 Jan 8;587:78-84. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.11.090. Epub 2021 Nov 27. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022. PMID: 34872003
-
Endothelial cell derived angiocrine support of acute myeloid leukemia targeted by receptor tyrosine kinase inhibition.Leuk Res. 2015 Sep;39(9):984-9. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2015.05.015. Epub 2015 Jul 2. Leuk Res. 2015. PMID: 26189107 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-talk between leukemic and endothelial cells promotes angiogenesis by VEGF activation of the Notch/Dll4 pathway.Carcinogenesis. 2013 Mar;34(3):667-77. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgs386. Epub 2012 Dec 13. Carcinogenesis. 2013. PMID: 23239744
-
VEGF targeted therapy in acute myeloid leukemia.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2011 Nov;80(2):241-56. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2010.09.009. Epub 2010 Oct 29. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2011. PMID: 21035354 Review.
-
[Angiogenesis in patients with hematologic malignancies].Onkologie. 2001 Sep;24 Suppl 5:75-80. doi: 10.1159/000055192. Onkologie. 2001. PMID: 11600818 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Endothelial progenitor cells in hematologic malignancies.Stem Cell Investig. 2016 Jul 1;3:26. doi: 10.21037/sci.2016.06.07. eCollection 2016. Stem Cell Investig. 2016. PMID: 27583252 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apatinib exhibits anti-leukemia activity in preclinical models of acute lymphoblastic leukemia.J Transl Med. 2018 Feb 28;16(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s12967-018-1421-y. J Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 29490645 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Targeting of the Leukaemia Microenvironment.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 26;22(13):6888. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136888. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34206957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myeloid malignancies and the microenvironment.Blood. 2017 Feb 16;129(7):811-822. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-09-670224. Epub 2016 Nov 15. Blood. 2017. PMID: 28064238 Free PMC article.
-
Glioblastoma and acute myeloid leukemia: malignancies with striking similarities.J Neurooncol. 2018 Jan;136(2):223-231. doi: 10.1007/s11060-017-2676-5. Epub 2017 Dec 1. J Neurooncol. 2018. PMID: 29196926 Review.
References
-
- Gallegos-Castorena S, Medina-Sanson A, Gonzalez-Ramella O, Sanchez-Zubieta F, Martinez-Avalos A. Improved treatment results in Mexican children with acute myeloid leukemia using a Medical Research Council (MRC)-acute myeloid leukemia 10 modified protocol. Leuk Lymphoma. 2009;50:1132–1137. doi: 10.1080/10428190902964768. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hann IM, Webb DK, Gibson BE, Harrison CJ. MRC trials in childhood acute myeloid leukaemia. Ann Hematol. 2004;83(Suppl 1):S108–S112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

