Remotely controllable liquid marbles
- PMID: 22833237
- PMCID: PMC3546392
- DOI: 10.1002/adma.201201885
Remotely controllable liquid marbles
Figures
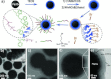


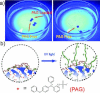
References
-
- Aussillous P, Quéré D. Nature. 2011;411:924. - PubMed
-
- Velev OD, Prevo BG, Bhatt KH. Nature. 2003;426:515. - PubMed
-
- Dorvee JR, Derfus AM, Bhatia SN, Sailor MJ. Nat. Mater. 2004;3:896. - PubMed
-
- Joanicot M, Ajdari A. Science. 2005;309:887. - PubMed
-
- Kotz KT, Gu Y, Faris GW. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005;127:5736. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

