Frizzled homolog proteins, microRNAs and Wnt signaling in cancer
- PMID: 22833265
- PMCID: PMC3940357
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.27746
Frizzled homolog proteins, microRNAs and Wnt signaling in cancer
Abstract
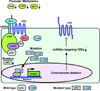
Wnt signaling pathways play important roles in tumorigenesis and are initiated by binding of Wnt to various receptors including frizzleds (FZDs). FZDs are one of several families of receptors comprised of FZD/LRP/ROR2/RYK in the Wnt signaling pathway. Expression of some FZD receptors are up regulated, thereby activating the Wnt signaling pathway and is correlated with cancer malignancy and patient outcomes (recurrence and survival) in many cancers. The FZD family contains ten genes in humans and their function has not been completely examined including the regulatory mechanisms of FZD genes in cancer. Knockdown of FZDs may suppress the Wnt signaling pathway resulting in decreased cell growth, invasion, motility and metastasis of cancer cells. Recently a number of microRNAs (miRNAs) have been identified and reported to be important in several cancers. MiRNAs regulate target gene expression at both the transcription and translation levels. The study of miRNA is a newly emerging field and promises to be helpful in understanding the pathogenesis of FZDs in cancer. In addition, miRNAs may be useful in regulating FZDs in cancer cells. Therefore, the aim of this review is to discuss current knowledge of the functional mechanisms of FZDs in cancer, including regulation by miRNAs and the potential for possible use of miRNAs and FZDs in future clinical applications.
Copyright © 2012 UICC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Frizzled Receptors in Tumors, Focusing on Signaling, Roles, Modulation Mechanisms, and Targeted Therapies.Oncol Res. 2021 Mar 16;28(6):661-674. doi: 10.3727/096504020X16014648664459. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Oncol Res. 2021. PMID: 32998794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
WNT/Frizzled signalling: receptor-ligand selectivity with focus on FZD-G protein signalling and its physiological relevance: IUPHAR Review 3.Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Mar;171(5):1195-209. doi: 10.1111/bph.12364. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24032637 Free PMC article. Review.
-
β-Catenin-dependent pathway activation by both promiscuous "canonical" WNT3a-, and specific "noncanonical" WNT4- and WNT5a-FZD receptor combinations with strong differences in LRP5 and LRP6 dependency.Cell Signal. 2014 Feb;26(2):260-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.11.021. Epub 2013 Nov 21. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24269653
-
The emerging understanding of Frizzled receptors.FEBS Lett. 2024 Aug;598(16):1939-1954. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.14903. Epub 2024 May 14. FEBS Lett. 2024. PMID: 38744670 Review.
-
Frizzled receptors (FZDs) in Wnt signaling: potential therapeutic targets for human cancers.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024 Aug;45(8):1556-1570. doi: 10.1038/s41401-024-01270-3. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024. PMID: 38632318 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
DLK1: a novel target for immunotherapeutic remodeling of the tumor blood vasculature.Mol Ther. 2013 Oct;21(10):1958-68. doi: 10.1038/mt.2013.133. Epub 2013 Jul 30. Mol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23896726 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Calretinin Expression in Human Mesothelioma Cells Reveals the Implication of the FAK and Wnt Signaling Pathways in Conferring Chemoresistance towards Cisplatin.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 29;20(21):5391. doi: 10.3390/ijms20215391. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31671889 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory effects of microRNA‑184 on osteosarcoma via the Wnt/β‑catenin signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Aug;18(2):1917-1924. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9184. Epub 2018 Jun 18. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29916553 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of exosome-derived microRNAs reveals insights of intercellular communication during invasion of breast, prostate and glioblastoma cancer cells.Cell Adh Migr. 2021 Dec;15(1):180-201. doi: 10.1080/19336918.2021.1935407. Cell Adh Migr. 2021. PMID: 34157951 Free PMC article.
-
Frizzled 8 promotes the cell proliferation and metastasis of renal cell carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2017 Sep 8;8(45):78989-79002. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20742. eCollection 2017 Oct 3. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29108281 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moon RT, Kohn AD, De Ferrari GV, Kaykas A. WNT and beta-catenin signaling: diseases and therapies. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5:691–701. - PubMed
-
- Clevers H. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell. 2006;127:469–480. - PubMed
-
- Katoh M, Katoh M. WNT signaling pathway and stem cell signaling network. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:4042–4045. - PubMed
-
- Lai SL, Chien AJ, Moon RT. Wnt/Fz signaling and the cytoskeleton: potential roles in tumorigenesis. Cell Res. 2009;19:532–545. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

