High-capacity selective uptake of cholesteryl ester from native LDL during macrophage foam cell formation
- PMID: 22833685
- PMCID: PMC3435541
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M026534
High-capacity selective uptake of cholesteryl ester from native LDL during macrophage foam cell formation
Abstract
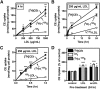
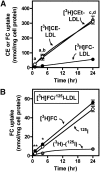
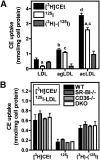
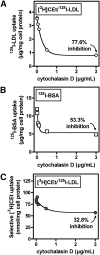
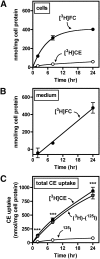
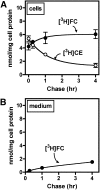
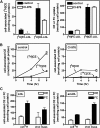
Macrophage foam cells are a defining pathologic feature of atherosclerotic lesions. Recent studies have demonstrated that at high concentrations associated with hypercholesterolemia, native LDL induces macrophage lipid accumulation. LDL particles are taken up by macrophages as part of bulk fluid pinocytosis. However, the uptake and metabolism of cholesterol from native LDL during foam cell formation has not been clearly defined. Previous reports have suggested that selective cholesteryl ester (CE) uptake might contribute to cholesterol uptake from LDL independently of particle endocytosis. In this study we demonstrate that the majority of macrophage LDL-derived cholesterol is acquired by selective CE uptake in excess of LDL pinocytosis and degradation. Macrophage selective CE uptake does not saturate at high LDL concentrations and is not down-regulated during cholesterol accumulation. In contrast to CE uptake, macrophages exhibit little selective uptake of free cholesterol (FC) from LDL. Following selective uptake from LDL, CE is rapidly hydrolyzed by a novel chloroquine-sensitive pathway. FC released from LDL-derived CE hydrolysis is largely effluxed from cells but also is subject to ACAT-mediated reesterification. These results indicate that selective CE uptake plays a major role in macrophage metabolism of LDL.
Figures


References
-
- 1984 The Lipid Research Clinics Coronary Primary Prevention Trial Results. II. The relationship of reduction in incidence of coronary heart disease to cholesterol lowering. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 251: 365–374 - PubMed
-
- 1994 Randomised trial of cholesterol lowering in 4444 patients with coronary heart disease: the Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study (4S). Lancet. 344: 1383–1389 - PubMed
-
- Nissen S. E., Nicholls S. J., Sipahi I., Libby P., Raichlen J. S., Ballantyne C. M., Davignon J., Erbel R., Fruchart J. C., Tardif J. C., et al. 2006. Effect of very high-intensity statin therapy on regression of coronary atherosclerosis: the ASTEROID trial. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 295: 1556–1565 - PubMed
-
- Webb N. R., Moore K. J. 2007. Macrophage-derived foam cells in atherosclerosis: lessons from murine models and implications for therapy. Curr. Drug Targets. 8: 1249–1263 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

