Recent and past musical activity predicts cognitive aging variability: direct comparison with general lifestyle activities
- PMID: 22833722
- PMCID: PMC3400047
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2012.00198
Recent and past musical activity predicts cognitive aging variability: direct comparison with general lifestyle activities
Abstract
Studies evaluating the impact of modifiable lifestyle factors on cognition offer potential insights into sources of cognitive aging variability. Recently, we reported an association between extent of musical instrumental practice throughout the life span (greater than 10 years) on preserved cognitive functioning in advanced age. These findings raise the question of whether there are training-induced brain changes in musicians that can transfer to non-musical cognitive abilities to allow for compensation of age-related cognitive declines. However, because of the relationship between engagement in general lifestyle activities and preserved cognition, it remains unclear whether these findings are specifically driven by musical training or the types of individuals likely to engage in greater activities in general. The current study controlled for general activity level in evaluating cognition between musicians and nomusicians. Also, the timing of engagement (age of acquisition, past versus recent) was assessed in predictive models of successful cognitive aging. Seventy age and education matched older musicians (>10 years) and non-musicians (ages 59-80) were evaluated on neuropsychological tests and general lifestyle activities. Musicians scored higher on tests of phonemic fluency, verbal working memory, verbal immediate recall, visuospatial judgment, and motor dexterity, but did not differ in other general leisure activities. Partition analyses were conducted on significant cognitive measures to determine aspects of musical training predictive of enhanced cognition. The first partition analysis revealed education best predicted visuospatial functions in musicians, followed by recent musical engagement which offset low education. In the second partition analysis, early age of musical acquisition (<9 years) predicted enhanced verbal working memory in musicians, while analyses for other measures were not predictive. Recent and past musical activity, but not general lifestyle activities, predicted variability across both verbal and visuospatial domains in aging. These findings are suggestive of different use-dependent adaptation periods depending on cognitive domain. Furthermore, they imply that early age of musical acquisition, sustained and maintained during advanced age, may enhance cognitive functions and buffer age and education influences.
Keywords: cognitive aging; lifestyle activities; modifiable factors of aging; music; training-induced changes.
Figures


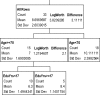
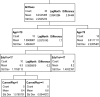
References
-
- Benton A., Sivan A., Hamsher K., Varney N., Spreen O. (ed.). (1994). Contributions to Neuropsychological Assessment: A Clinical Manual. New York: Oxford University Press
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

