2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin enhances CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity in an aryl hydrocarbon receptor-dependent manner
- PMID: 22834477
- PMCID: PMC6319626
- DOI: 10.3109/00498254.2012.707790
2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin enhances CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity in an aryl hydrocarbon receptor-dependent manner
Abstract
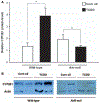
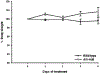
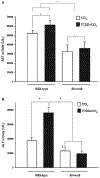
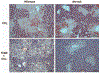
Cytochrome P4502E1 (CYP2E1) is involved in the biotransformation of several low molecular weight chemicals and plays an important role in the metabolic activation of carcinogens and hepatotoxins such as CCl(4). Induction of CYP2E1 is exerted mainly at posttranscriptional levels through mRNA and protein stabilization, and there is little evidence of xenobiotic induction at the transcriptional level. Previously, we reported microarray analysis data suggesting a decrease in Cyp2e1 gene expression on Ahr-null livers when compared to wild-type mouse livers. The goal of the present study was to determine whether 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) increased mouse CYP2E1 levels in an AhR-dependent manner and the impact on CCl(4)-induced hepatotoxicity. TCDD treatment induced CYP2E1 mRNA and protein levels in mouse liver, and this effect was aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR)-dependent. Moreover, TCDD pre-treatment increased the CCl(4)-induced alanine aminotransferase (ALT) activity, the extent of CCl(4)-induced necrosis, and the number of sinusoidal cells in wild-type animals, while this potentiating effect was not observed in Ahr-null mice. In conclusion, this study revealed that TCDD, probably in an AhR-dependent manner, exacerbated CCl(4)-induced hepatotoxicity through induction of CYP2E1.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Role of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) in overall retinoid metabolism: Response comparisons to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) exposure between wild-type and AHR knockout mice.Reprod Toxicol. 2021 Apr;101:33-49. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2021.02.004. Epub 2021 Feb 16. Reprod Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33607186
-
A chimeric aryl hydrocarbon receptor knockout mouse model indicates that aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation in hematopoietic cells contributes to the hepatic lesions induced by 2,3,7, 8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1999 Jul 1;158(1):33-40. doi: 10.1006/taap.1999.8681. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10387930
-
Knockout of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor results in distinct hepatic and renal phenotypes in rats and mice.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2013 Oct 15;272(2):503-18. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2013.06.024. Epub 2013 Jul 13. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23859880
-
Altered thyroxin and retinoid metabolic response to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in aryl hydrocarbon receptor-null mice.Arch Toxicol. 2005 May;79(5):260-7. doi: 10.1007/s00204-004-0626-4. Epub 2004 Nov 17. Arch Toxicol. 2005. PMID: 15902423
-
Gene expression profile by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in the liver of wild-type (AhR+/+) and aryl hydrocarbon receptor-deficient (AhR-/-) mice.J Vet Med Sci. 2006 Jul;68(7):663-8. doi: 10.1292/jvms.68.663. J Vet Med Sci. 2006. PMID: 16891777
Cited by
-
Dioxin Receptor Adjusts Liver Regeneration After Acute Toxic Injury and Protects Against Liver Carcinogenesis.Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 5;7(1):10420. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-10984-w. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28874739 Free PMC article.
-
2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) increases necroinflammation and hepatic stellate cell activation but does not exacerbate experimental liver fibrosis in mice.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2016 Nov 15;311:42-51. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2016.09.025. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27693115 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring transcriptomic databases to identify and experimentally validate tissue-specific consensus reference gene for gene expression normalization in BALB/c mice acutely exposed to 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin.Curr Res Toxicol. 2025 Apr 27;8:100234. doi: 10.1016/j.crtox.2025.100234. eCollection 2025. Curr Res Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40391131 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia Routes Tryptophan Homeostasis Towards Increased Tryptamine Production.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 19;12:590532. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.590532. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33679737 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson LM, Angel M. (1980). Induction of dimethylnitrosamine demethylase activity in mouse liver by polychlorinated biphenyls and 3-methylcholanthrene. Biochem Pharmacol 29:1375–1383. - PubMed
-
- Braeuning A, Köhle C, Buchmann A, Schwarz M. (2011). Coordinate regulation of cytochrome P450 1a1 expression in mouse liver by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor and the beta-catenin pathway. Toxicol Sci 122:16–25. - PubMed
-
- Cheung C, Akiyama TE, Kudo G, Gonzalez FJ. (2003). Hepatic expression of cytochrome P450s in hepatocyte nuclear factor 1-alpha (HNF1alpha)-deficient mice. Biochem Pharmacol 66:2011–2020. - PubMed
-
- Cheung C, Yu AM, Ward JM, Krausz KW, Akiyama TE, Feigenbaum L, Gonzalez FJ. (2005). The cyp2e1-humanized transgenic mouse: role of cyp2e1 in acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Drug Metab Dispos 33:449–457. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
