Odontogenic myxoma with diffuse calcifications: a case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 22837042
- PMCID: PMC3597162
- DOI: 10.1007/s12105-012-0387-y
Odontogenic myxoma with diffuse calcifications: a case report and review of the literature
Abstract
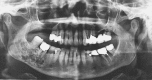
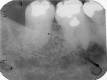
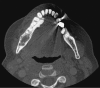
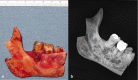
This is a case report of an unusual odontogenic myxoma with calcifications, one of three reported in the literature. It had a typical radiographic appearance although it presented in an older patient. The presence of osteo-cementum-like calcification raises other differential diagnoses but does not in and of itself mitigate the diagnosis. The patient has not shown recurrence 14 months after resection and 11 months after reconstruction and continues to be closely monitored.
Figures


References
-
- White SC, Pharoah MJ. Oral radiology: principles and interpretation. St. Louis: Mosby; 2004.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

