Identification of the Cdc48•20S proteasome as an ancient AAA+ proteolytic machine
- PMID: 22837385
- PMCID: PMC3923512
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1224352
Identification of the Cdc48•20S proteasome as an ancient AAA+ proteolytic machine
Abstract
Proteasomes are the major energy-dependent proteolytic machines in the eukaryotic and archaeal domains of life. To execute protein degradation, the 20S core peptidase combines with the AAA+ ring of the 19S regulatory particle in eukarya or with the AAA+ proteasome-activating nucleotidase ring in some archaea. Here, we find that Cdc48 and 20S from the archaeon Thermoplasma acidophilum interact to form a functional proteasome. Cdc48 is an abundant and essential double-ring AAA+ molecular machine ubiquitously present in archaea, where its function has been uncertain, and in eukarya where Cdc48 participates by largely unknown mechanisms in diverse cellular processes, including multiple proteolytic pathways. Thus, proteolysis in collaboration with the 20S peptidase may represent an ancestral function of the Cdc48 family.
Figures
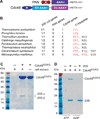
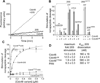


Comment in
-
Cell biology. An ancient portal to proteolysis.Science. 2012 Aug 17;337(6096):813-4. doi: 10.1126/science.1227301. Science. 2012. PMID: 22904006 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sauer RT, Baker TA. AAA+ proteases: ATP-fueled machines of protein destruction. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2011;80:587–612. - PubMed
-
- Voges D, Zwickl P, Baumeister W. The 26S proteasome: a molecular machine designed for controlled proteolysis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1999;68:1015–1068. - PubMed
-
- Zwickl P, Ng D, Woo KM, Klenk HP, Goldberg AL. An archaebacterial ATPase, homologous to ATPases in the eukaryotic 26 S proteasome, activates protein breakdown by 20 S proteasomes. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:26008–26014. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

