Tyrosine 201 is required for constitutive activation of JAK2V617F and efficient induction of myeloproliferative disease in mice
- PMID: 22837531
- PMCID: PMC3433092
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2011-09-380808
Tyrosine 201 is required for constitutive activation of JAK2V617F and efficient induction of myeloproliferative disease in mice
Abstract
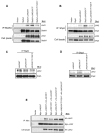
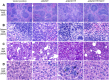
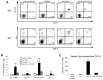
The JAK2V617F mutation has been detected in most cases of Ph-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs). The JAK2V617F protein is a constitutively activated tyrosine kinase that leads to transformation of hematopoietic progenitors. Previous studies have shown that several tyrosine residues within JAK2 are phosphorylated on growth factor or cytokine stimulation. However, the role of these tyrosine residues in signaling and transformation mediated by JAK2V617F remains unclear. In this study, we sought to determine the role of tyrosine 201, which is a potential binding site for Src homology 2 domain-containing proteins, in JAK2V617F-induced hematopoietic transformation by introducing a tyrosine-to-phenylalanine point mutation (Y201F) at this site. We observed that the Y201F mutation significantly inhibited cytokine-independent cell growth and induced apoptosis in Ba/F3-EpoR cells expressing JAK2V617F. The Y201F mutation also resulted in significant inhibition of JAK2V617F-mediated transformation of hematopoietic cells. Biochemical analyzes revealed that the Y201F mutation almost completely inhibited constitutive phosphorylation/activation of JAK2V617F. We also show that the Y201 site of JAK2V617F promotes interaction with Stat5 and Shp2, and constitutive activation of downstream signaling pathways. Furthermore, using a BM transduction/transplantation approach, we found that tyrosine 201 plays an important role in the induction of MPNs mediated by JAK2V617F.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The Jak2V617F oncogene associated with myeloproliferative diseases requires a functional FERM domain for transformation and for expression of the Myc and Pim proto-oncogenes.Blood. 2008 Apr 1;111(7):3751-9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-07-102186. Epub 2008 Jan 23. Blood. 2008. PMID: 18216297 Free PMC article.
-
Three Tyrosine Residues in the Erythropoietin Receptor Are Essential for Janus Kinase 2 V617F Mutant-induced Tumorigenesis.J Biol Chem. 2017 Feb 3;292(5):1826-1846. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.749465. Epub 2016 Dec 20. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 27998978 Free PMC article.
-
Tyrosine-phosphorylated SOCS3 negatively regulates cellular transformation mediated by the myeloproliferative neoplasm-associated JAK2 V617F mutant.Cytokine. 2019 Nov;123:154753. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2019.154753. Epub 2019 Jun 27. Cytokine. 2019. PMID: 31255914
-
JAK2 and MPL mutations in myeloproliferative neoplasms.Acta Haematol. 2008;119(4):218-25. doi: 10.1159/000140634. Epub 2008 Jun 20. Acta Haematol. 2008. PMID: 18566540 Review.
-
JAK-2 mutations and their relevance to myeloproliferative disease.Curr Opin Hematol. 2007 Jan;14(1):43-7. doi: 10.1097/00062752-200701000-00009. Curr Opin Hematol. 2007. PMID: 17133099 Review.
Cited by
-
The thrombopoietin receptor, MPL, is critical for development of a JAK2V617F-induced myeloproliferative neoplasm.Blood. 2014 Dec 18;124(26):3956-63. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-07-587238. Epub 2014 Oct 22. Blood. 2014. PMID: 25339357 Free PMC article.
References
-
- James C, Ugo V, Le Couedic JP, et al. A unique clonal JAK2 mutation leading to constitutive signaling causes polycythemia vera. Nature. 2005;434(7037):1144–1148. - PubMed
-
- Levine RL, Wadleigh M, Cools J, et al. Activating mutation in the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, and myeloid metaplasia with myelofibrosis. Cancer Cell. 2005;7(4):387–397. - PubMed
-
- Baxter EJ, Scott LM, Campbell PJ, et al. Acquired mutation of the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in human myeloproliferative disorders. Lancet. 2005;365(9464):1054–1061. - PubMed
-
- Kralovics R, Passamonti F, Buser AS, et al. A gain-of-function mutation of JAK2 in myeloproliferative disorders. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(17):1779–1790. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

