Subnetwork-based analysis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia identifies pathways that associate with disease progression
- PMID: 22837534
- PMCID: PMC3460686
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2012-03-416461
Subnetwork-based analysis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia identifies pathways that associate with disease progression
Abstract
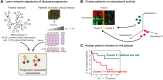
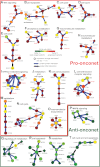
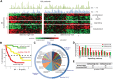
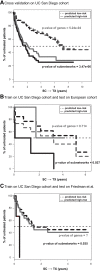
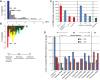
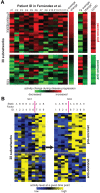
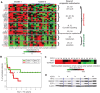
The clinical course of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is heterogeneous. Several prognostic factors have been identified that can stratify patients into groups that differ in their relative tendency for disease progression and/or survival. Here, we pursued a subnetwork-based analysis of gene expression profiles to discriminate between groups of patients with disparate risks for CLL progression. From an initial cohort of 130 patients, we identified 38 prognostic subnetworks that could predict the relative risk for disease progression requiring therapy from the time of sample collection, more accurately than established markers. The prognostic power of these subnetworks then was validated on 2 other cohorts of patients. We noted reduced divergence in gene expression between leukemia cells of CLL patients classified at diagnosis with aggressive versus indolent disease over time. The predictive subnetworks vary in levels of expression over time but exhibit increased similarity at later time points before therapy, suggesting that degenerate pathways apparently converge into common pathways that are associated with disease progression. As such, these results have implications for understanding cancer evolution and for the development of novel treatment strategies for patients with CLL.
Figures
References
-
- Hallek M, Cheson BD, Catovsky D, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a report from the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia updating the National Cancer Institute-Working Group 1996 guidelines. Blood. 2008;111(12):5446–5456. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hamblin TJ, Davis Z, Gardiner A, Oscier DG, Stevenson FK. Unmutated Ig V(H) genes are associated with a more aggressive form of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 1999;94(6):1848–1854. - PubMed
-
- Damle RN, Wasil T, Fais F, et al. Ig V gene mutation status and CD38 expression as novel prognostic indicators in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 1999;94(6):1840–1847. - PubMed
-
- Rassenti LZ, Huynh L, Toy TL, et al. ZAP-70 compared with immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene mutation status as a predictor of disease progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(9):893–901. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

