State of the art in silico tools for the study of signaling pathways in cancer
- PMID: 22837650
- PMCID: PMC3397482
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms13066561
State of the art in silico tools for the study of signaling pathways in cancer
Abstract
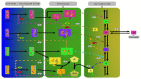
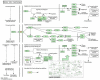
In the last several years, researchers have exhibited an intense interest in the evolutionarily conserved signaling pathways that have crucial roles during embryonic development. Interestingly, the malfunctioning of these signaling pathways leads to several human diseases, including cancer. The chemical and biophysical events that occur during cellular signaling, as well as the number of interactions within a signaling pathway, make these systems complex to study. In silico resources are tools used to aid the understanding of cellular signaling pathways. Systems approaches have provided a deeper knowledge of diverse biochemical processes, including individual metabolic pathways, signaling networks and genome-scale metabolic networks. In the future, these tools will be enormously valuable, if they continue to be developed in parallel with growing biological knowledge. In this study, an overview of the bioinformatics resources that are currently available for the analysis of biological networks is provided.
Keywords: bioinformatics; cancer; networks; pathways; systems biology.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Proteomic and computational methods in systems modeling of cellular signaling.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2006 Jun;7(3):135-45. doi: 10.2174/138920106777549722. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2006. PMID: 16789899 Review.
-
MOVE: a multi-level ontology-based visualization and exploration framework for genomic networks.In Silico Biol. 2007;7(1):35-59. In Silico Biol. 2007. PMID: 17688427
-
Principles and methods of integrative genomic analyses in cancer.Nat Rev Cancer. 2014 May;14(5):299-313. doi: 10.1038/nrc3721. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24759209 Review.
-
Pathway Tools version 19.0 update: software for pathway/genome informatics and systems biology.Brief Bioinform. 2016 Sep;17(5):877-90. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbv079. Epub 2015 Oct 10. Brief Bioinform. 2016. PMID: 26454094 Free PMC article.
-
Pathway mapping tools for analysis of high content data.Methods Mol Biol. 2007;356:319-50. doi: 10.1385/1-59745-217-3:319. Methods Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 16988414 Review.
Cited by
-
A rule-based model of insulin signalling pathway.BMC Syst Biol. 2016 Jun 1;10(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s12918-016-0281-4. BMC Syst Biol. 2016. PMID: 27245161 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schena M., Shalon D., Davis R.W., Brown P.O. Quantitative monitoring of gene expression patterns with a complementary DNA microarray. Science. 1995;270:467–470. - PubMed
-
- Patterson S.D., Aebersold R.H. Proteomics: The first decade and beyond. Nat. Genet. 2003;33:311–323. - PubMed
-
- Vieites J.M., Guazzaroni M.-E., Beloqui A., Golyshin P.N., Ferrer M. Metagenomics approaches in systems microbiology. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2009;33:236–255. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

