Effect of calcium and potassium on antioxidant system of Vicia faba L. Under cadmium stress
- PMID: 22837652
- PMCID: PMC3397484
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms13066604
Effect of calcium and potassium on antioxidant system of Vicia faba L. Under cadmium stress
Abstract
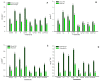
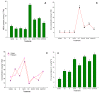
Cadmium (Cd) in soil poses a major threat to plant growth and productivity. In the present experiment, we studied the effect of calcium (Ca(2+)) and/or potassium (K(+)) on the antioxidant system, accumulation of proline (Pro), malondialdehyde (MDA), and content of photosynthetic pigments, cadmium (Cd) and nutrients, i.e., Ca(2+) and K(+) in leaf of Vicia faba L. (cv. TARA) under Cd stress. Plants grown in the presence of Cd exhibited reduced growth traits [root length (RL) plant(-1), shoot length (SL) plant(-1), root fresh weight (RFW) plant(-1), shoot fresh weight (SFW) plant(-1), root dry weight (RDW) plant(-1) and shoot dry weight (SDW) plant(-1)] and concentration of Ca(2+), K(+), Chlorophyll (Chl) a and Chl b content, except content of MDA, Cd and (Pro). The antioxidant enzymes [peroxidase (POD) and superoxide dismutase (SOD)] slightly increased as compared to control under Cd stress. However, a significant improvement was observed in all growth traits and content of Ca(2+), K(+), Chl a, Chl b, Pro and activity of antioxidant enzymes catalase (CAT), POD and SOD in plants subjected to Ca(2+) and/or K(+). The maximum alleviating effect was recorded in the plants grown in medium containing Ca(2+) and K(+) together. This study indicates that the application of Ca(2+) and/or K(+) had a significant and synergistic effect on plant growth. Also, application of Ca(2+) and/or K(+) was highly effective against the toxicity of Cd by improving activity of antioxidant enzymes and solute that led to the enhanced plant growth of faba bean plants.
Keywords: antioxidant; faba bean; heavy metal; nutrient content; photosynthetic pigments.
Figures

References
-
- Sanitá di Toppi L., Gabbrielli R. Response to cadmium in higher plants. Environ. Exp. Bot. 1999;41:105–130.
-
- Yang X.E., Long X.X., Ye H.B., He Z.L., Calvert D.V., Stoffella P.J. Cadmium tolerance and hyperaccumulation in a new Zn hyperaccumulating plant species (Sedum alfredii Hance) Plant Soil. 2004;259:181–189.
-
- Leita L., de Nobili M., Cesco C., Mondini C. Analysis of intercellular cadmium forms in roots and leaves of bush bean. J. Plant Nutr. 1996;19:527–533.
-
- Mishra S., Srivastava S., Tripathi R.D., Govindarajan R., Kuriakose S.V., Prasad M.N.V. Phytochelatin synthesis and response of antioxidants during cadmium stress in Bacopa monnieri L. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2006;44:25–37. - PubMed
-
- Das P., Samantaray S., Rout G.R. Studies on cadmium toxicity in plants: A review. Environ. Pollut. 1997;98:29–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

