Serum insulin-like growth factor binding protein 6 (IGFBP6) is increased in patients with type 1 diabetes and its complications
- PMID: 22837797
- PMCID: PMC3403553
Serum insulin-like growth factor binding protein 6 (IGFBP6) is increased in patients with type 1 diabetes and its complications
Abstract
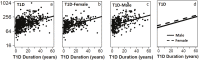
Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins (IGFBPs) are associated with insulin resistance and accelerated micro- and macro-vascular complications of diabetes. We investigated the relationship between serum levels of IGFBP6 in type-1 diabetes (T1D) patients and diabetic complications. In this study, IGFBP6 was measured in the sera from 697 T1D patients and 681 healthy controls using a Luminex assay. Mean serum levels of IGFBP6 were higher in T1D patients than controls matched for sex and age (119.7 vs 130.6 ng/ml, p < 10(-4)). Subject age, sex and duration of disease have a significant impact on serum IGFBP6 levels in both T1D patients and healthy controls. Patients with complications have significantly higher mean serum IGFBP6 than patients without any complication (p = 3.5x10(-6)). More importantly, conditional logistic regression analysis suggested that T1D patients are more likely to have very high levels of serum IGFBP6 (in the 4(th) quartile) (OR = 1.7) than healthy controls. Furthermore, T1D patients with various complications are more likely to have very high levels of serum IGFBP6 (in the 4(th) quartile) than patients without any complication (OR = 1.7 - 22.9). These results indicate the clinical importance of measuring IGFBP6 to the better management of T1D patients.
Keywords: Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins (IGFBPs); complications; diabetes; insulin resistance.
Figures



References
-
- Firth SM, Baxter RC. Cellular actions of the insulin-like growth factor binding proteins. Endocr Rev. 2002;23:824–854. - PubMed
-
- Hwa V, Oh Y, Rosenfeld RG. The insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (IGFBP) superfamily. Endocr Rev. 1999;20:761–787. - PubMed
-
- Korevaar TIM, Ragazzoni F, Weaver A, Karavitaki N, Grossman AB. IGF2-induced hypoglycemia unresponsive to everolimus. QJM: Int J Med. 2012 doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcr249. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
